Hi all. I am very glad that you visited my site. And today, we will talk about what a short circuit is and what kind of short circuits there are.
A short circuit is a connection (contact) of two or more points (conductors) of an electrical circuit with different potential values.
Different potentials are when there is phase and zero in an AC network, or plus and minus in a DC network.
Now let's look at what types there are short circuit.
IN single-phase network There can only be two types of short circuit:
1. phase and zero - this type of closure very often occurs in simple living conditions. For example, with the onset of winter it becomes cold, and many people try to warm up with the help of electric heaters.
But few people pay attention to the sockets into which these same heaters are plugged in. It often happens that the sockets are not designed for the currents that the heaters consume, or often the sockets may have poor contact.
Because of this, sockets and plugs begin to heat up. As a result of prolonged heating, the insulation of the wires is destroyed. And at one fine moment two, already exposed, conductors may touch, and a short circuit will result.

2. phase and grounding - this is when phase wire, somehow begins to contact the grounded frame of any electrical equipment. Either electric water heater, lamp, machine and so on.
It also happens that the housing may be zeroed, then such a short circuit can be attributed to the first case.
But in situations in which a short circuit occurs, it can be much more:
1. single-phase fault– phase and zero. I have already described this type above, so let’s move on to the next one.
2. two-phase - this is when two phases are connected to each other. Often happens on overhead power lines. This phenomenon has probably been seen by every person in his life. When on the street strong wind and begins to loosen the wires, and receives a small fireworks. In industrial enterprises, such a short circuit often occurs in power circuits.

3. two-phase and ground - this, of course, happens less often, but it still happens. An example when two phases can connect to each other, and at the same time also contact the ground.
4. three-phase - this is when all three phases are somehow closed together. Such a short circuit will occur when some conductive object falls or touches all three phases at the same time.
What could be the consequences of short circuit currents?
During a short circuit, the current instantly increases, which leads to strong heating and melting of metals. Splashes of this metal scatter in all directions, and all this is accompanied by a bright flash and fire. Which can easily lead to a fire and very serious consequences.
In ordinary home conditions, if you do not choose the right short circuit protection, you can really lose a lot. Starting from your home and furniture, and ending with your own life and the lives of the people living with you under the same roof.

In enterprises, short circuit currents can lead to emergency situations, damage to equipment, and people can also suffer from this. But enterprises usually use several protections at once, which practically eliminates the occurrence of short circuits.
That's all I wanted to say. If you have any questions, ask them in the comments. If the article was useful to you, then share it with your friends on in social networks and subscribe for updates. Until next time.
Sincerely, Alexander!
A short circuit occurs when current-carrying parts of different potentials or phases are connected to each other. A short circuit can also form on the equipment body connected to the ground. This phenomenon is also typical for electrical networks and electrical receivers.
Causes and effects of short circuit current
The causes of a short circuit can be very different. This is facilitated by damp or aggressive environment, in which it deteriorates significantly. A closure may result mechanical influences or personnel errors during repairs and maintenance.
The essence of the phenomenon lies in its name and represents a shortening of the path along which the current passes. As a result, current flows past the resistive load. At the same time, it increases to unacceptable limits if the protective shutdown does not work.
However, power outage may not occur even if there are protective equipment. This situation occurs when the short circuit is very far away and significant resistance makes the current insufficient to trigger protective devices. However, this current is quite enough to ignite the wires and cause a fire.

In such situations great importance have so-called time-current characteristics characteristic of circuit breakers. Here, current cutoff and thermal releases that protect against overloads play an important role. These systems have absolutely different time operation, therefore, slow action of thermal protection can lead to the formation of a burning arc and damage to conductors located nearby.
Short circuit currents have an electrodynamic and thermal effect on equipment and electrical installations, which ultimately leads to their significant deformation and overheating. In this regard, it is necessary to make calculations of short-circuit currents in advance.
How to calculate short circuit current using the formula
Calculation of these currents, as a rule, is carried out if it is necessary to check the operation of equipment in extreme situations. The main purpose is to determine the suitability of protective automatic devices. In order to correctly calculate the short circuit current, first of all, you need to know exactly the metal from which the conductor is made. For calculations you will also need the length of the wire and its cross-section.

For determining resistivity it is necessary to know the active resistance index Rп, the value of which consists of the resistivity of the wire multiplied by its length. The value of inductive reactance Xp is calculated based on the specific inductive reactance, taken as 0.6 Ohm/km.
The Zt indicator is the total resistance of the phase winding installed in the transformer on the low voltage. Thus, timely preliminary calculations will help to avoid serious damage to electrical equipment caused by a short circuit.

Calculations make it possible to accurately determine which circuit breaker will provide the most effective protection from short circuits. However, all the necessary measurements can be made using a special device, which is precisely designed to determine these values. To take measurements, the device is connected to the network and switched to the required mode.
Network short circuit protection
When designing any energy system, specially trained electrical engineers use technical reference books, tables, graphs and computer programs perform its analysis on the operation of the circuit in various modes, including:
1. idle;
2. rated load;
3. emergency situations.
The third case is especially dangerous, when faults occur in the network that can damage equipment. Most often, they are associated with a “metallic” short-circuit of the supply circuit, when electrical resistances of fractions of an ohm are randomly connected between different potentials of the supplied voltage.
Such modes are called short circuit currents or abbreviated as “short circuit”. They occur when:
malfunctions of automation and protection;
errors of service personnel;
equipment damage due to technical aging;
spontaneous impacts of natural phenomena;
sabotage or acts of vandals.
Short circuit currents significantly exceed the rated loads for which the electrical circuit is designed. Therefore, they simply burn out weak points in the equipment, destroy it, and cause fires.

In addition to thermal destruction, they also have a dynamic effect. Its manifestation is clearly shown in the video:
In order to prevent the development of such accidents during operation, they begin to fight against them even at the stage of creating the electrical equipment design. To do this, theoretically calculate the possibility of occurrence of short circuit currents and their magnitude.
This data is used to further create the project and select the power elements and protective devices of the circuit. They continue to work with them constantly during equipment operation.
Currents of possible short circuits are calculated using theoretical methods with varying degrees of accuracy acceptable for reliable creation of protection.
What electrical processes are the basis for calculating short circuit currents?
Initially, let us focus on the fact that any type of applied voltage, including direct, alternating sinusoidal, pulsed or any other random one, creates emergency currents that repeat the image of this form or change it depending on the applied resistance and the action of collateral factors. Designers have to provide for all this and take it into account in their calculations.
The occurrence and action of short circuit currents can be assessed by:
Ohm's law;
the magnitude of the power characteristic of the power applied from the voltage source;
structure used electrical diagram electrical installations;
the value of the total applied resistance to the source.
Action of Ohm's law
The basis for calculating short circuits is the principle that determines that the current strength can be calculated from the applied voltage if divided by the value of the connected resistance.
It also applies when calculating rated loads. The only difference is that:
during optimal performance of the electrical circuit, the voltage and resistance are practically stabilized and change slightly within the operating technical standards;
In case of accidents, the process occurs spontaneously and randomly. But it can be foreseen and calculated using developed methods.
Voltage source power
With its help, the power and energy potential of performing destructive work by short-circuit currents is assessed, and the duration of their flow and magnitude are analyzed.

Let's consider an example when the same piece copper wire with a cross-section of one and a half square mm and a length of half a meter, they were first connected directly to the terminals of the Krona battery, and after a while they were inserted into the phase and neutral contacts of a household outlet.
In the first case, a short circuit current will flow through the wire and the voltage source, which will heat the battery to such a state that it will damage its performance. The power of the source is not enough to burn the connected jumper and break the circuit.
In the second case they will work automatic protection. Let's assume that they are all faulty and jammed. Then the short circuit current will pass through home wiring, will reach the entrance panel to the apartment, entrance, building and via cable or overhead line power transmission will reach the supply transformer substation.
As a result, a fairly long circuit with big amount wires, cables and their connections. They will significantly increase electrical resistance our short. But even in this case, there is a high probability that it will not withstand the applied power and will simply burn out.
Electrical circuit configuration
When powering consumers, voltage is supplied to them different ways, For example:
through the potentials of the positive and negative terminals of a constant voltage source;
phase and zero single-phase household network 220 volt;
three-phase circuit 0.4 kV.
In each of these cases, insulation failures may occur at various locations, causing short circuit currents to flow through them. Only for three-phase circuit AC current short circuits are possible between:
all three phases at the same time - called three-phase;
any two phases between themselves - phase-to-phase;
any phase and zero - single-phase;
phase and ground - single-phase to ground;
two phases and ground - two-phase to ground;
three phases and ground - three phase to ground.
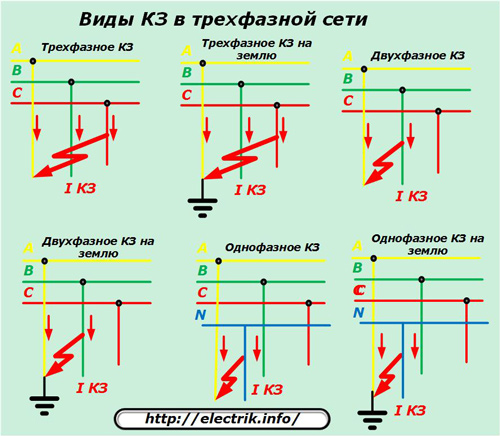
When creating a power supply project for equipment, all these modes must be calculated and taken into account.
Effect of Electrical Circuit Resistance
The length of the line from the voltage source to the point where the short circuit occurs has a certain electrical resistance. Its value limits short circuit currents. The presence of transformer windings, chokes, coils, and capacitor plates add inductive and capacitive resistances that form aperiodic components that distort the symmetrical shape of the fundamental harmonics.
Existing methods for calculating short-circuit currents allow them to be calculated with sufficient accuracy for practice using previously prepared information. The actual electrical resistance is already assembled circuit can be measured using the method. It allows you to clarify the calculation and make adjustments to the choice of protection.

Basic documents on calculating short circuit currents
1. Methodology for calculating short-circuit currents
It is well presented in the book by A.V. Belyaev “Selection of equipment, protection and cables in 0.4 kV networks”, published by Energoatomizdat in 1988. The information covers 171 pages.
The book provides:
sequence of calculation of short-circuit currents;
taking into account the current-limiting effect electric arc at the site of damage;
principles for selecting protective equipment based on calculated current values.
The book publishes reference Information By:
circuit breakers and fuses with analysis of the characteristics of their protective properties;
selection of cables and equipment, including installations for protecting electric motors, power assemblies, input devices generators and transformers;
deficiencies of protection individual species circuit breakers;
features of the use of remote relay protection;
examples of solving design problems.
2. Guidelines RD 153—34.0—20.527—98
This document defines:
methods for calculating short-circuit currents in symmetrical and asymmetrical modes in electrical installations with voltages up to and above 1 kV;
methods for testing electrical devices and conductors for thermal and electrodynamic resistance;
methods for testing the switching capacity of electrical devices.
The instructions do not cover the issues of calculating short-circuit currents in relation to relay protection and automation devices with specific operating conditions.
3. GOST 28249-93
The document describes short circuits that occur in AC electrical installations and the methodology for calculating them for systems with voltages up to 1 kV. It has been in effect since January 1, 1995 in the territories of Belarus and Kyrgyzstan. Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Ukraine.
The state standard defines general methods calculations of short-circuit currents at the initial and any arbitrary time point for electrical installations with synchronous and asynchronous machines, reactors and transformers, overhead and cable power lines, busbars, complex load nodes.
Technical standards for the design of electrical installations are determined by current state standards and agreed upon by the Interstate Council on Standardization, Metrology, and Certification.
Sequence of designer actions for calculating short circuit currents
Initially, you should prepare the information necessary for the analysis, and then carry out the calculations. After installation of the equipment, the process of putting it into operation and during operation, the correct choice and operability of the protections are checked.
Collection of initial data
Any diagram can be reduced to a simplified form when it consists of two parts:
1. voltage source. For a 0.4 kV network, its role is played by the secondary winding of the power transformer;
2. power supply line.
The necessary characteristics are collected for them.
Transformer data for calculating short-circuit currents
You need to find out:
value of short circuit voltage (%) - Us;
short circuit loss (kW) - Pk;
rated voltages on the windings of the high and low sides (kV. V) - Uin, Unn;
phase voltage on the low side winding (V) - Eph;
rated power (kVA) — Snt;
impedance single-phase short circuit current (mOhm) - Zt.
Supply line data for calculating short-circuit currents
These include:
brand and number of cables indicating the material and cross-section of the cores;
total length of the route (m) - L;
inductive reactance (mOhm/m) - X0;
total resistance for the phase-zero loop (mOhm/m) - Zpt.
This information for the transformer and line is concentrated in reference books. The shock coefficient Kud is also taken there.
Calculation sequence
Based on the found characteristics, calculate for:
transformer - active and inductive resistance (mOhm) - Rt, Xt;
lines - active, inductive and impedance (mOhm).
three-phase fault and shock (kA);
single-phase short circuit (kA).
Based on the values of the last calculated currents, they select circuit breakers and other consumer protection devices.
Designers can calculate short-circuit currents manually using formulas, lookup tables and graphs, or using special computer programs.

On real energy equipment Once commissioned, all currents, including rated and short-circuit currents, are recorded by automatic oscilloscopes.

Such oscillograms allow you to analyze the progress of emergency modes, correct operation of power equipment and protective devices. They accept effective measures to increase the reliability of the electrical circuit consumers.
An electrical circuit is usually called an electrical circuit through which current flows. A circuit may consist, for example, of a battery powering a light bulb, or of many elements interconnected, for example in your computer. A circuit can consist of an unlimited number of elements and the current always enters one contact at the beginning of the circuit and leaves one contact at the end of the circuit.
For reference:
Many people call an open circuit a short circuit. It is necessary to clearly understand that a short circuit is essentially a bridge (jumper) for the passage of current along the shortest path at the location of the short circuit, bypassing some of the elements of the entire electrical circuit.
Typically, a short circuit has a very small resistance - this leads to the flow of a large current from the power source (which can damage it). If the power wire is directly connected to ground (possibly shorting the plus and minus of the power supply), the fuse usually blows, and if it is not there, the power source may burn out. This is a short circuit.
If something turns on and stops working again when you move the elements of the circuit, this is called an open circuit and the break occurs precisely at the moment when the device is not working. That is, no current flows and the circuit does not work.

Current movement and electron movement in DC circuits
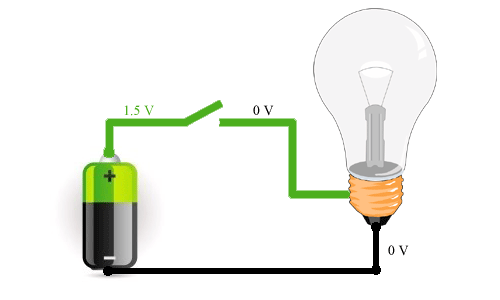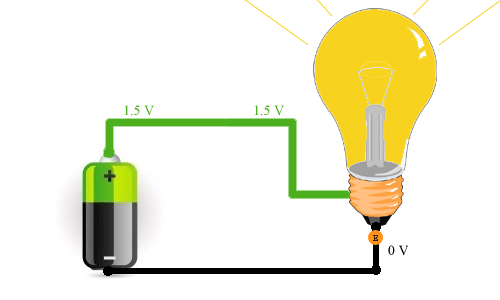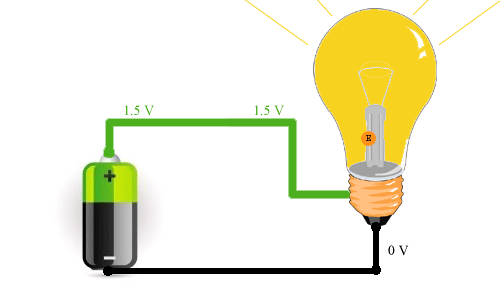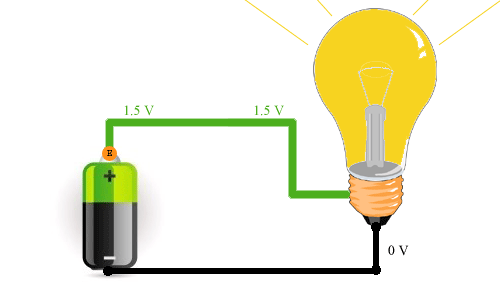
In the picture above you can see how it proceeds electricity and how electrons move. As you can see, electrons move from the minus (negative terminal of the power supply) to the positive (positive terminal). This is how electric current actually moves. Most of the time, people believed that charge carriers were positively charged particles, which meant they had to move from the positive to the negative terminal. This is how we usually imagine the usual movement of current. If it’s easier for you to imagine that the current flows from plus to minus, then there’s nothing wrong with that, it doesn’t change the essence of the process.
In chains with alternating current, the polarity of the current source is constantly changing, so in such a circuit electrons move in both forward and reverse directions. In other articles on our website we will talk more about direct and alternating current.
Good afternoon, dear readers of the Electrician's Notes website.
I have long wanted to write an article about short circuits. But somehow they didn’t get around to it.
Today I decided because the latest events that happened on distribution substation our enterprise.
Earlier in the articles we said that they cause short circuits, or short circuits for short.
A short circuit is one of the most severe and dangerous species damage.
You will ask why? Read below.
What is a short circuit?
Wikipedia answers this question that a short circuit is:

Read the definition.
Now let's take a closer look at what happens to the parameters of the electrical installation at the time of a short circuit.
When a short circuit occurs, the voltage on the power source, or more correctly called the EMF, is short-circuited through a small (small value) resistance of cable and overhead lines, windings of transformers and generators. Hence the name "short circuit".
In a “short-circuited” circuit, a very large current appears, which is called short-circuit current.
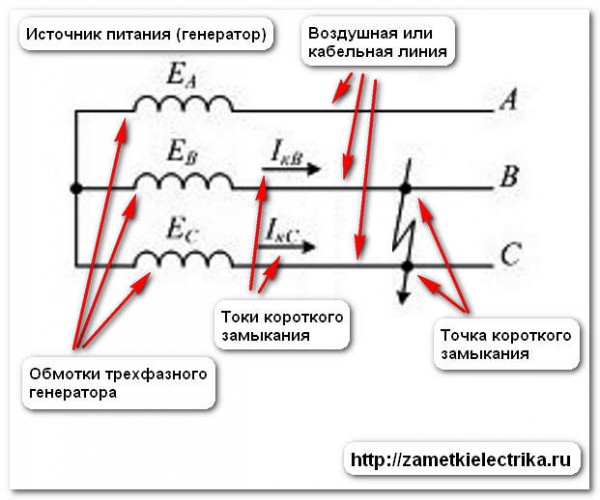
Let's consider the classification of short circuits.
Short circuits are divided by the number of closed phases:
- three-phase short circuits
- two-phase short circuits
- single-phase short circuits
Short circuits are divided by circuit:
- with the ground
- without land
Short circuits are divided by the number of shorted points in the network:
- at one point
- at two points
- at several points (more than two)

Example
Let's look at an example.
Let's assume that our consumer is powered from a substation through an overhead power line (OHL). The supply line is transit, so the consumer is powered by a tap from the overhead line at point “O”.

The dotted line number 2 shows the voltage level along the entire overhead line before a short circuit occurs.
The figure shows that the voltage at any point electrical network equal to the difference EMF source supply and voltage drop in the electrical circuit to the point we need.
For example, the voltage at point “O” can be calculated using the formula :
Uо = E - I*Zo, where
- E - EMF of the power source, in our case the generator
- Zo is the total resistance of the overhead lines from the power source to point “O” (consists of active and reactive resistance)
- I is the current flowing through the overhead line in this moment time.
Let's assume that for some reason there is a short circuit on the overhead line, but outside our tap. Let's call this short circuit point the letter "K".
What happens at the moment of a short circuit?
At the moment of a short circuit, no more passes through the overhead line rated current, and the short circuit current is large, so the voltage drop across each element of the electrical circuit increases. Namely, on the resistance Zo and Zк.
The most greatest decrease voltage will be at the point of short circuit, i.e. at point "K". At other points of the overhead line, distant from the short circuit, the voltage will drop slightly less (this can be seen in the figure - line number 1).
In one of my articles I provided a visual example. Follow the link and get acquainted with the materials.
Consequences of a short circuit
We have already found out that at the moment of a short circuit there is a sharp increase in the current value and a decrease in voltage, which leads to the following consequences.
1. Destruction
Let's remember a little physics.
According to the law of the famous physicist Joule-Lenz, a short circuit current, flowing through the active resistance of an electrical circuit for some time, releases heat in it, which is calculated by the formula:
![]()
At the point of a short circuit, this heat, as well as the electric arc flame, causes enormous destruction. And the greater the short circuit current and the time it takes to pass through the circuit, the greater the destruction will be.
To make it clear to you how large-scale these destructions are, below I will give examples from my practice.
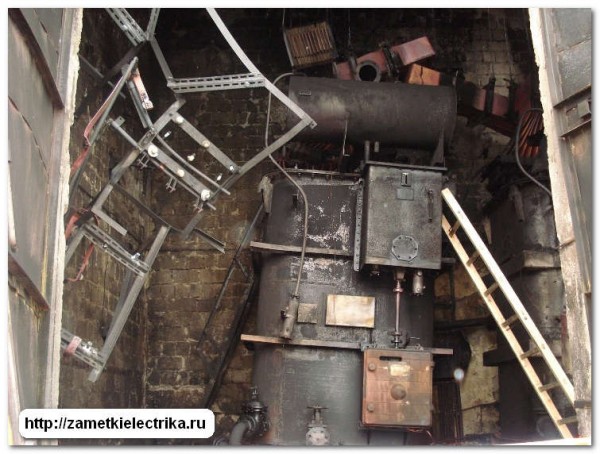


On-load tap-changer drive. A short circuit occurred in the winding of an asynchronous motor
2. Insulation damage
During the passage of short circuit current through undamaged lines, they heat up above the limit permissible temperature, which leads to damage to their insulation.
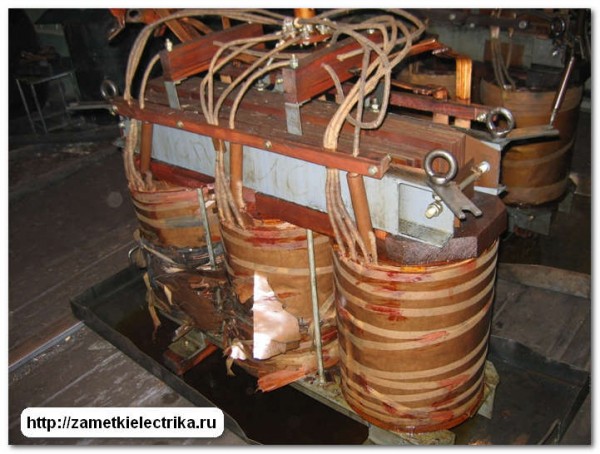

Active part of the transformer. The short circuit occurred due to insulation damage
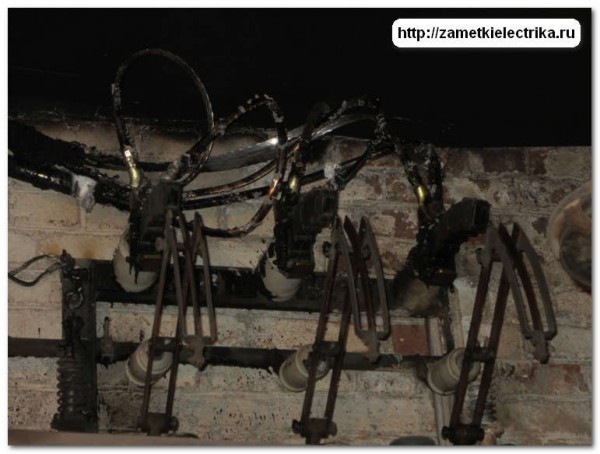


Cable short circuit. Consequences
3. Consumers and power receivers
A decrease in voltage during a short circuit disrupts the normal operation of consumers and electrical receivers.
For example, an asynchronous one may stop altogether when the network voltage decreases, because the moment of its rotation may be less than the moment of resistance and friction of the mechanisms.
Also violated normal operation and lighting stops. Here I think there is no need to explain.
Look visual video about the causes and consequences of a short circuit in a 400 (V) electrical installation at one of our substations:
P.S. At the end of the article on the topic of short circuit, I would like to confirm what was said at the beginning of my article, that short circuit is the most dangerous and looking heavy damage that requires an instant and quick response and disconnection of the damaged section of the circuit.
