Hello, Dear guests Electrician's Notes website.
We have already devoted many articles to the topic of electricity metering, but we did not have enough time to understand the structure and operating principle of the electric meter.
Therefore, today’s article is devoted to the operating principle of single-phase and three-phase meters electrical energy.
As you already know, according to the operating principle, electric meters are divided into 2 types:
- induction
- electronic
Let's take a closer look at the operating principle of each type of counter.
Operating principle of an induction electric meter

1 - current or series winding(coil)
2 - parallel coil (winding) or voltage coil
3 - counting mechanism in the form of a worm gear
4 — permanent magnet to create braking and smooth disk movement
5 - aluminum disk
Fi is the magnetic flux that is created by the load current
Фu is the magnetic flux that is created by the current in the voltage coil
The electric meter consists of 2 coils (windings): a voltage coil and a current coil, the electromagnets of which are located at an angle of 90° relative to each other in space. In the gap between these electromagnets there is an aluminum disk, which is mounted on bearings and thrust bearings on the lower and upper sides. A worm is installed on the axis of the disk, which transmits rotation to the counting mechanism (drum) through gears.
The current coil is connected in series in the circuit and consists of large quantity turns. Such a coil is wound with a thick wire, respectively, straight rated current electricity meter.
The voltage coil is connected in parallel to the circuit and consists of a large number of turns. Reeling in thin wire with a diameter of approximately 0.06 - to 0.12 (mm).
When an alternating voltage is applied to the voltage coil and when load current flows through the current coil, alternating magnetic fluxes Фi and Фu are induced in the gap, which induce eddy currents in the aluminum disk. When these flows interact with eddy currents in the disk, a torque arises - the disk begins to rotate.
The number of revolutions of the aluminum disk per certain time- this will be our consumed electricity.
When the load current increases (for example, we connected an additional load to the network), more torque will appear in the current coil and the disk will rotate faster.
IN electronic electricity meter converter converts input analog signals from current and voltage sensors into digital pulse code. This code is sent to the microcontroller, where it is decrypted and calculated, and then displays the amount of electricity consumed on the display of the electric meter.
P.S. Thank you for your attention. Author of the site "Electrician's Notes".
Electric meter, more precisely, an electrical energy consumption meter is a special device designed to account for the electrical energy consumed by a load. According to its technical idea, it is a combination of a meter for consumed electrical energy with a counting mechanism that displays the readings. There are electric meters for measuring energy of constant or alternating current. AC electricity meters are available in single-phase and three-phase types. According to the operating principle electric meters can be inductive and electronic.
A brief history of the creation of an electric meter
In 1885, the Italian Galileo Ferraris (1847-1897) made an interesting observation of the rotation of a solid rotor in the form of a metal disk or cylinder under the influence of two out-of-phase alternating current fields. This discovery served as the starting idea for creating an induction motor and at the same time opened up the possibility of developing induction meter.
The first meter of this type was created in 1889 by Hungarian Otto Titutz Blati, who worked at the Ganz plant in Budapest, Hungary. They patented the idea electric meter for alternating currents (patent issued in Germany, No. 52.793, patent obtained in the USA, No. 423.210).
In such a device, Blati was able to obtain an internal phase shift of almost 90°, which allowed the meter to display watt-hours quite accurately. The electric meter of this model already used a braking permanent magnet, which provided a wide range of measurements of the amount of energy consumed, and a cyclometric-type register was also used.
Subsequent years were marked by many improvements, manifested in reducing the weight and size of the device, expanding the range permissible loads, compensation for changes in load factor, voltage and temperature values. The friction in the supports of the rotating rotor of the counter was significantly reduced by replacing the thrust bearings with ball bearings; later, double stones were used and magnetic bearings. The stable operation life of the meter has significantly increased due to increased technical characteristics brake electromagnetic system and non-use of oil in the rotor supports and counting mechanism. Much later, a three-phase induction meter was created for industrial consumers, which used a combination of two or three measurement systems installed on one, two or even three separate disks.
Scheme for connecting the meter induction type
Induction type general case is extremely simple and consists of two windings (current and voltage) and a terminal block to which their contacts are routed. Conditional diagram, through which a single-phase electric meter is connected, in a standard electrical panel apartment buildings has the following form:
Here, phase “A” is indicated by a yellow line, phase “B” by green, phase “C” by red, neutral wire"N" – lines blue color a, the grounding conductor “PE” is a yellow-green line. The batch switch is now often replaced by a more modern one two-pole circuit breaker with overload protection. It should be noted that between the connection diagram of the induction type meter and similar scheme connecting an electronic meter there are no fundamental differences.
The conventional diagram for connecting an electric meter in a three-phase four-wire network with a voltage of 380 volts looks like:
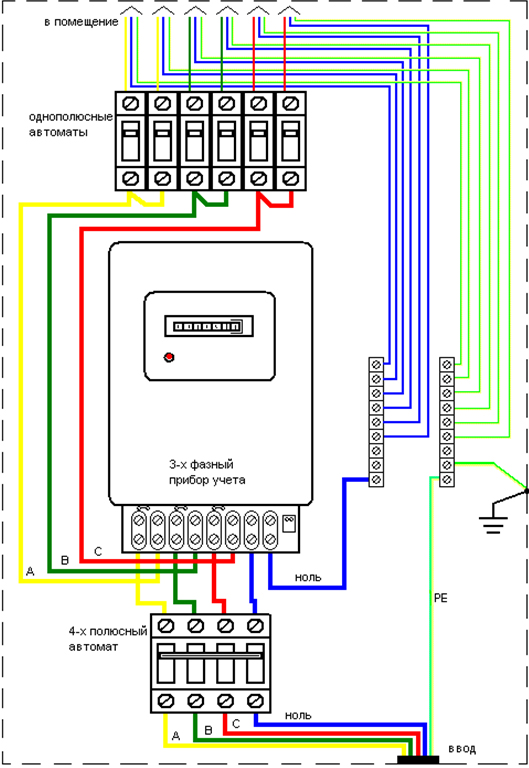
Here color designations similar to the previous meter connection diagram for a single-phase network.
It is important to observe the direct phase sequence three-phase network on the meter contact block. It can be determined using a phase indicator or a VAF device. In direct order, the alternation of voltage phases is as follows: ABC, BCA, CAB (if you go clockwise). In reverse order, the alternation of voltage phases is as follows: ASV, SVA, VAS. In this case, an additional error is created and self-propelling of the rotor of the induction meter for active energy occurs. IN electric meter reactive energy, the reverse order of alternation of load phases and voltages leads to rotation of the rotor in the opposite direction.
Scheme electrical connections single-phase induction electric meter
In the diagram, red lines indicate phase wire and a current coil, and the blue color is the neutral wire and the voltage coil.
Electrical diagram connections three-phase meter induction type at direct connection in a four-wire 380 volt network:
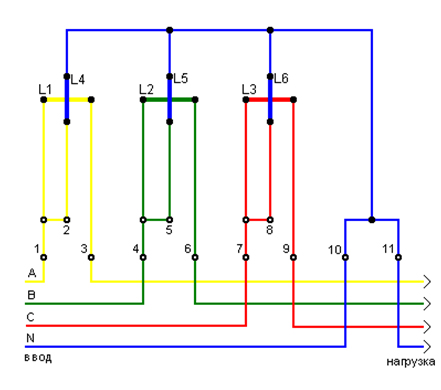
Here: phase “A” denotes yellow, phase "B" - green, phase "C" - red, neutral wire "N" - blue; L1, L2, L3 – indicate current coils; L4, L5, L6 - indicate voltage coils; 2, 5, 8 – voltage contacts; 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11 – contacts for connecting external electrical wiring to a three-phase meter.
Operating principle and design of an induction electricity meter
The current winding, connected in series with the electricity consumer, has a small number of turns, which are wound with a thick wire corresponding to the rated current of this counter. This ensures a minimum of its resistance and introduces a current measurement error.
The voltage winding, connected in parallel with the load, has a large number of turns (8000 - 12000), which are wound with a thin wire, which reduces current consumption idle move counter. When connected to it AC voltage, and the load current flows in the current winding, electromagnetic fields are closed through the aluminum disk, which is the rotor, inducing so-called eddy currents in it. These currents interact with the electromagnetic field and create a torque that drives the movable aluminum disk.
A permanent magnet creating a magnetic flux through the meter disk creates the effect of a braking (counteracting) torque.
Constancy of the disk rotation speed is achieved with a balance of rotating and braking forces.
The number of rotor revolutions per hour will be proportional to the energy consumed, which is equivalent to the fact that the value of the steady-state uniform speed of rotation of the disk is proportional to the power consumed if the torque acting on the disk is adequate to the power of the consumer to which the meter is connected.
Friction in the kinematic pairs of the induction counter mechanism creates errors in measurement readings. The influence of friction is especially significant at small (up to 5-10% of the nominal value) loads for an induction meter, when the magnitude of the negative error can be 12 - 15%. To reduce the influence of friction forces in an induction counter, use special device, which is called a friction compensator.
Essential Parameter electric energy meter alternating current - the sensitivity threshold of the device, which implies the value of the minimum power, expressed as a percentage of the rated value, at which the meter rotor begins to rotate steadily. In other words, the sensitivity threshold is minimum consumption electricity that the meter is able to record.
In accordance with GOST, the value of the sensitivity threshold for induction meters various classes accuracy should be no more than 0.5 - 1.5%. The level of sensitivity is set by the value of the compensating torque and the braking torque, which is created by a special anti-self-propelled device.
Operating principle of an electronic meter
Induction meters for electrical energy consumption, despite their simplicity and low cost, have a number of disadvantages, which are based on the use of mechanical moving elements that have insufficient stability of parameters during long-term operation of the device. An electronic electricity meter does not have these disadvantages, has a low sensitivity threshold, and higher accuracy in measuring energy consumption.
True, building an electronic meter requires the use of highly specialized integrated circuits(IC), which can multiply current and voltage signals and form the resulting value in a form convenient for processing by a microcontroller. For example, microcircuits that convert active power- to the value of the pulse repetition rate. The total number of received pulses integrated by the microcontroller is directly proportional to the electricity consumed.

Block diagram of an electronic meter
No less important for the full operation of an electronic meter is the presence of all kinds of service functions, such as remote access to the meter for remote monitoring of readings, determination of day and night energy consumption and many others. The use of a digital display allows the user to programmatically set various formats for displaying information, for example, display information on the amount of energy consumed over a certain interval, set different tariffs, etc.
To perform certain non-standard functions, for example, matching signal levels, additional ICs will be required. Currently, the production of specialized microcircuits - power-to-proportional frequency converters - and specialized microcontroller devices having a similar converter on a single chip has begun. But, more often than not, they are too expensive for use in household induction meters. Therefore, many global microcontroller manufacturers are developing specialized low-cost microcircuits specifically designed for such applications.
What type does it have? electrical circuit diagram of the meter using the simplest digital option on the most inexpensive (less than a dollar) 8-bit microcontroller from Motorola? In the solution under consideration, all the minimum required functions of the device are implemented. It is based on the use of an inexpensive IC that converts power into pulse frequency of the KR1095PP1 type and an 8-bit microcontroller device MC68HC05KJ1. With this counter architecture, the microcontroller needs to sum up the received number of pulses, display information on the display and protect the device in various abnormal modes. The described meter is in fact a digital functional analogue of existing mechanical meters, adapted for further improvement.
Electrical circuit diagram of the simplest digital electricity meter
Signals equivalent to the voltage and current values in the network are received from sensors and supplied to the input of the converter. The microcircuit multiplies the input signals, forming an instantaneous value of power consumption. This value is sent to the microcontroller and converted into watt hours. As data accumulates, the counter readings on the LCD change. The presence of frequent failures in the device's power supply voltage leads to the need to use EEPROM to ensure the safety of meter readings. Since power supply failures are the most common abnormal situation, such protection is required in any electronic meter.
Electrical circuit diagram of the meter(digital computer) is given below. Through connector X1, the 220 V mains voltage and the electrical consumer are connected. Voltage and current sensors generate signals supplied to the KR1095PP1 microcircuit of the converter, which has optocoupler isolation of the frequency output. The core of the counter is the MC68HC05KJ1 microcontroller manufactured by Motorola, manufactured in a 16-pin package (DIP or SOIC package) and equipped with 1.2 KB of ROM and 64 bytes of RAM. To save the accumulated amount energy consumed During power failures, an EEPROM with a small amount of memory 24C00 (16 bytes) from Microchip is used. The display is a 7-segment 8-bit LCD, which is controlled by any inexpensive microcontroller that exchanges data with the central microcontroller via SPI or I2C protocols and is connected via the X2 connector.
The underlying operating algorithm for the counter required less than 1 KB of memory and less than half of all I/O ports on the MC68HC05KJ1 microcontroller. His technical capabilities enough to supplement the meter with some service functions, for example, the ability to combine meters into local network via RS-485 interface. This feature allows you to obtain data on energy consumption in service center and remotely turn off electricity if the consumer does not pay. A network containing such meters can be equipped with a residential apartment house. All meter readings via the network will be sent remotely to the control center.
Of practical interest is the use of a family of 8-bit microcontrollers with a chip containing built-in FLASH memory. This allows it to be programmed directly on the assembled board. It also provides security against hacking program code and the convenience of updating software without performing installation work.
Digital computer for electronic electricity meter
More interesting is the option of an electronic electricity meter without the use of external EEPROM and expensive external non-volatile RAM. In this case, in the event of an emergency, it is possible to record readings and other service information in the internal FLASH memory of the microcontroller. This additionally ensures the required data confidentiality, which cannot be ensured if an external crystal is used that is not protected from unauthorized access by unauthorized persons. Such an electronic electricity meter with any level of complexity and functionality can be created using a Motorola microcontroller from the HC08 family with FLASH memory built into the main chip.
Making the transition to digital remote automatic means accounting and control of electricity consumption is a matter of time. The technical and consumer advantages of such systems are obvious. Their cost will invariably decrease. And even if a simple microcontroller is used, such an electronic electricity meter has obvious advantages: high reliability due to the complete absence of moving parts; miniature; the possibility of producing a meter in a housing taking into account the interior features of modern residential buildings; increasing the verification interval several times; high maintainability and extreme ease of maintenance and operation. Even small additional hardware and software costs in the simplest digital meter can complement it with a number of service functions that are fundamentally absent from all mechanical electricity meters, for example, the use of multi-tariff charging for energy consumed, the ability to implement automated metering and control of electricity consumption.
See also diagrams.
We all know why an electricity meter is needed - to correctly account for electricity consumption. Based on the electric meter readings, payments are made “for light”. In this article we would like to tell readers about the design and operating principle of an electricity meter. For you, we will consider both the electronic model and the old model - induction.
Induction
Old electricity meters consist of the following elements:
- Series winding, also called current coil. Consists of several turns of thick wire.
- Parallel winding (voltage coil). On the contrary, it is constructed from a large number of turns of thin wire.
- Counting mechanism. Installed on the axle of an aluminum disk.
- A permanent magnet, the purpose of which is to brake and ensure smooth movement of the disk.
- Aluminum disc. Mounted on bearings and thrust bearings.
As can be seen in the diagram, the design of an induction electricity meter is quite simple. As for the operating principle, it is also simple. First, alternating voltage is applied to the parallel winding (voltage coil) and then flows to the second, current coil. Magnetic eddy currents arise between the two electromagnets of the coils, which, in fact, contribute to the rotation of the disk. The higher the current, the faster the disk will spin. In turn, the counting mechanism works according to the following principle: rotation from the disk is transmitted to the drum through a worm gear (this is facilitated by a worm installed on the axis of the disk, which transmits rotation through a gear, as can be seen in the diagram above).
See clearly how it works induction electricity meter, you can watch the video below:
Operation diagram of an old type electricity meter
Please note that the operating principle single-phase meter The old model's electricity supply is similar to the three-phase model.
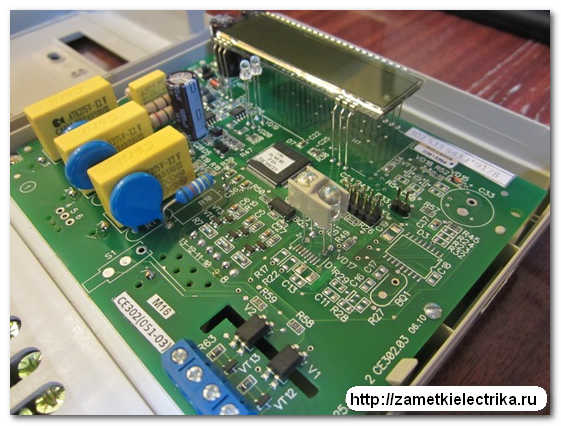
Electronic
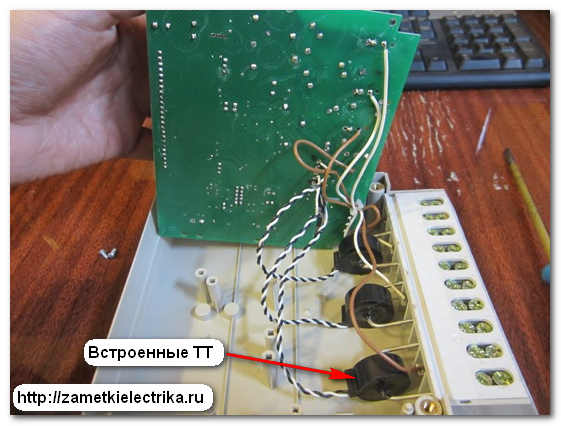
An electronic meter, for example, has neither a disk nor a worm gear. The design of the new type of electricity meters is shown in the diagram and photo below:

