Nowadays, almost every home has at least one energy-saving light bulb installed. Incandescent light bulbs have been replaced by fluorescent and LED analogues, which have a number of undeniable advantages. They are used literally everywhere - they come in a wide range and make it possible to adapt them to any needs, both in industrial and residential premises.
And now the long-awaited purchase is finally in their hands, people screw in new light bulbs to replace the old, hot and yellow old ones - and rejoice in high-quality and economical light. However, sometimes in the off state there is a very interesting effect– the emitter begins to blink at a certain frequency, which is terribly annoying. In this article we will try to understand the reasons and offer solutions to the problem when Powersave lamp blinks unpleasantly.
Flickering fluorescent light bulb
Blinking is very noticeable at night in residential areas, especially in bedrooms. Even a slight wink from the housekeeper is very annoying and prevents you from falling asleep normally. Most people will unscrew it the next morning and go to the store to ask for a replacement. And what a surprise it will be when, regardless of the number of replacements of these lamps, they will still regularly irritate your eyes. Therefore, do not rush to get rid of them.
Why does the energy-saving lamp blink when the lights are off? The point is that it is not the light bulb itself that is to blame. To understand the problem, we first need to understand the device itself. Unlike incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps operate on DC. In order to straighten alternating current from the network, the emitter housing contains a special element with the simple name “rectifier”.
It almost completely removes all impulses in the network, smoothing them out. And this is precisely the reason why the energy-saving lamp blinks after being turned off.
Illuminated switch. Switches with a small glowing light are very convenient in large, dark rooms. And in 95% of cases, it is in this room that the light bulb, when the light is off, creates a light disco. This occurs due to processes in the switch itself, due to which the light is lit. small LED.

This small LED only lights up when the main contacts in the switch are open, i.e. when the room is dark. To do this, a very small current must flow through a small point - it is so insignificant that they do not react to it and electric meter. But the capacitor in the luminescent version, which is designed to start lighting after a certain charge has been collected, senses it. This small current gradually accumulates in it, and upon reaching a certain point, the capacitor tries to start the lamp. This is the most common problem.

Of course, this charge is very small for a full start, so a short flash follows, and the capacitor begins to gain a new charge, and the light blinks again.
When an additional light bulb is installed in the switch, this process is inevitable. Depending on the power and manufacturer, there may be differences in the brightness of the flashes and their frequency. This is a rather harmful effect for such a delicate mechanism, because the starter is designed for a strictly defined number of starts of the light bulb - as a result of which it can fail much earlier than the time allotted by the manufacturer. There are several ways to stop them from blinking:
- The easiest way is to simply remove the backlight. This can be done either by completely replacing the switch with the most common one (which can cost a pretty penny if there are 5-6 such problems in the house), or by physically turning off the backlight.

- To do this, turn off the lights in the house using the switch, having previously stocked up on a working flashlight. Disassemble the required switch, carefully cut the wires that go to the small light bulb (do not confuse it with power cables!). Then insulate everything, assemble the switch and turn on the lights in the house. It shouldn't blink anymore.
- Use a parallel connection of a regular incandescent lamp on the same network. If you install it in front of the fluorescent lamp, then it will collect this small current - the incandescent lamp is indifferent to it. However, then there is no point in saving, and it is not always practically possible to fulfill this point.
- Instead of an incandescent lamp, you can use an additional resistance called a resistor. At parallel connection it can be hidden in a special distribution box out of sight. A resistance of 30–60 kOhm and a power of about 2 W will be enough for household light bulbs; there are plenty of such resistors in special stores.

In addition to additional lighting in the switch, a similar effect can be observed in a system that contains complex devices that pass very little current through them to operate. These include various timers, dimmers, photocells and motion detectors. If possible, we get rid of them too.
LED light blinking
The time has come when fluorescent lamps are gradually starting to leave our everyday life. They are being replaced by the most modern LED solutions. They are even more economical, practically do not heat up and shine with a light that is very pleasant to the eye, adding even more comfort to your home. And, despite their rather high cost, they are found almost everywhere. The emitters in the lamps are new, but problems remain? Does the LED lamp blink even when the contacts in the switch are open? No problem - let's figure out why.

Here the symptoms expand a little - in addition to the fact that it flickers, a very weak glow of the crystals themselves can be observed, but it is very noticeable in dark room and not very pleasing to the eye.
- How to remove blinking? The reason is still the additional lighting in the switch. The same principle works here - either replace the switch completely, which is very expensive in total, or physically disconnect this small module by disassembling the switch.
- Why is the LED lamp blinking? To absorb the small current that has a bad effect on our light bulb, in addition to the resistor, you can also use a small capacitor. For household purposes suitable option, with characteristics of about 600 volts and a capacity of about 0.01 µF. If you use a capacitor designed for a standard network voltage of 220 volts, then it may fail during a sudden voltage drop and will have to be replaced. It is better to immediately take a good supply, their cost is low.

It has no polarity; you can connect wires to any of its legs. The main thing is that the connection is made parallel to the LED light bulb. As a result, the accumulation of slipping current in the capacitor, we get a non-blinking diode light bulb.
- The previous point is relevant for switches that have only one backlit button. However, if there are two such keys, how to remove the flickering of LED lamps? They each control their own groups, these groups are influenced by each individual luminous module in the switch itself. Therefore, it is not enough to connect a resistor or capacitor to only one group. How to eliminate flickering of LED lamps in this case? A similar action must be performed for all emitters that are powered by each key.

- But it also happens that the lamp blinks after turning off, even when additional modules are installed. Standard scheme connections - when the contacts in the switch open, the phase is switched off, but the zero remains constant. If a constant phase is applied to the light bulb, then the device is under constant load, and the starter continues to charge, even with conventional switches without backlight. This common reason Why is the LED blinking?
- If next to a wire connected according to all the rules, there is another one in the wall power cable with weak insulation, it can transfer potential to our light bulb. Moreover, if a resistor or capacitor is connected to the point of contact of the wires in the wall, it will not help at all to avoid the unpleasant effect. The solution is to place the resistance as close as possible to the light bulb to eliminate flickering.
Conclusion
Thus, in 95% of cases why a light bulb blinks, either the switches are to blame or the assembled circuit. Don't panic, this problem can be solved quite simply. By purchasing just a few inexpensive radio components and armed with heat shrink or electrical tape, you can eliminate annoying blinking in absolutely all cases in a few minutes. Be sure to follow safety precautions when working with current, remember that it is deadly to an unprotected by special means person.
If the LED lamp blinks when it is on, then most likely it is faulty; contact the seller and exchange it for a new one under warranty. This is the only reason why the LED lamp blinks when it is on. Try to fix the problem as quickly as possible; it greatly reduces the service life of your product.
Most users in their homes have already replaced conventional incandescent lamps with energy saving ones. However, when purchasing economical lamps, you have to deal with an unusual phenomenon.
It turns out that the energy-saving and LED light bulbs in chandeliers and lamps begin to blink weak flashes(even with the lights off). This is especially noticeable indoors dark time days. However, when replacing an economical lamp with the most common incandescent light bulbs, the phenomenon immediately disappears.
It all started when a neighbor came to me and started complaining that the store sold him defective energy-saving lamps. Yesterday he says he bought and installed five light bulbs in a five-arm chandelier. They work great, they shine well, but in the evening when I got ready to go to bed, I turned off the chandelier and I slept, talking like at a disco, all these five lights flash periodically.
What could be the reason? We came to his house, and indeed, when the chandelier is turned on, the lamps shine normally, but when the switch is off, they begin to blink, and that’s it. Well, I think there might be a bad contact somewhere in the chandelier or something else.
After examining everyone contact connections connecting the chandelier everything was in order, no questions arose at all. But there was one point - the switch was with LED backlight. So, Why is the energy saving lamp blinking? after shutdown? Let's find out in this article.
How modern energy-saving lamps work
With a question , we’ll look at it a little later, now we’ll figure out how modern energy-saving lamps work.
Did you know that, unlike incandescent lamps, fluorescent and LED lamps operate on permanent source power supply, that is, they operate on a constant (rectified) voltage. How can you ask? After all, the lamp is supplied AC voltage 220 V, there are no rectifiers in sockets or chandeliers. I assure you, there is, and this rectifier is located inside any modern lamp.
Inside each energy-saving lamp, between the base and the tube, there is an electronic board (in professional language they are called electronic ballasts), thanks to which they work.
An alternating voltage is supplied to the input of a special rectifier (diode bridge), and at the output we have a constant or rectified voltage.
I will not go into all the details of the operation of these circuits, but in order to smooth out the ripples, a special smoothing capacitor is installed. Just because of this capacitor . And in what case this happens, and under what circumstances, let's look at it below.
Why does a switched off energy saving lamp blink?
Let's return to the first section of the article, with a neighbor, a backlit switch and energy-saving lamps. I would like to draw your attention to the backlit switch, since that is where the problem lies.

What physical processes occur in illuminated switches? When the switch is turned on, its power contacts are closed. When the switch is in the off position, the lamp in the backlight lights up (because that’s why it’s installed there).
And if the lamp is on, it means there is a leak through it electricity, which moves along the following path: network - backlight lamp - chandelier with lamp - network. This current is very small (about hundredths of an ampere) and does not affect the overall network load (the electric meter does not respond to it).

The current flowing through the backlight serves as charging for the capacitor in electronic circuit light bulbs. As soon as it receives a sufficient level of recharging to turn on, the circuit starts up, which is why a flash is produced. Further, after a short flash, the capacitor is immediately discharged, and the process is repeated again.

When using a backlit switch, there is a flickering effect that bothers everyone so much. Therefore when used illuminated switch and a compact fluorescent lamp produces this blinking effect. You turn off the switch, the light in the key lights up and the lamp begins to flash periodically.
A similar situation is with low-power power supplies for LED strips. “At the input” of the source, exactly the same diode rectifier and capacitor are provided.
Accordingly, a small compensating current flows in the backlit switches, and the capacitor has time to recharge. In this regard, turned off LED Strip Light starts working in smoldering mode with periodic flashes of light.
How to eliminate the cause of blinking energy-saving lamps
- 1) Probably the most simple solution will remove the backlight. To do this, open the switch cover and disconnect the wires that power the backlight. Or you can simply cut this wire (do not confuse it with power wires).
In this case, when the switch is turned off, the current that recharges the capacitor will not flow accordingly - the lamp does not blink.
- 2) Do not use a backlit switch. Replace all backlit switches with regular ones where energy-saving lamps are used.
- 3) Connect a regular incandescent lamp in parallel with an energy-saving lamp. This method allows you to eliminate the blinking of energy-saving lamps, since the current that charged the capacitor will go to the filament.
But I believe that this method does not really have a place to exist, since the point of all this saving and modernization. Moreover, there is not always room in the lamp to install an incandescent lamp next to an energy-saving one. But that's my personal opinion.
- 4) There are switches in which the backlight is an integral part, for example, it works as a decorative element. What to do in this situation?
If energy saving lamp flashes after switching off, one way to solve the problem is to connect an additional resistance (resistor) in parallel with the lamp.

The resistor should be 2 W with a nominal resistance of 50 kOhm. The cost of such a resistor is a penny, about 10 rubles. You can purchase it at any amateur radio store.

On normal work lamps, this resistor has no effect, but when the switch is off, that is, when the backlight is on, this resistor will consume the current that recharges the capacitor in starting circuit lamps.

They are becoming increasingly popular among consumers different kinds LED devices. Their use allows for better and more diverse lighting. Lamps of this type are constantly being improved, thanks to new technologies and materials used in production. They are superior to other types in all respects lighting fixtures. However, sometimes situations arise when the LED lamp blinks. This can happen immediately after purchase or during operation, in the on or off state.
Design and principle of operation of an LED lamp
Before considering the causes of malfunctions, you should general outline get acquainted with the design LED lamp. It is quite simple and consists of a base, a metal base, and a platform on which the LEDs are installed. They are covered with a plastic protective hemisphere. The design also includes a driver that is directly involved in the operation and conversion of current.
The operating principle of such devices is based on the emission of light as a result of the connection between the cathode and anode. Both electrodes are separated by a semiconductor made of special materials. It is these materials that directly affect the quality of light, its color scheme and other indicators.
LED lamp blinks when turned on
Immediately after switching on, the lamp lights up a short time, and then goes out. In most of these cases, the cause is a faulty trigger mechanism that is unable to provide adequate in full converting and supplying current, cannot overclock the entire system. This problem can be solved by simply replacing the starter.

The switched on lamp does not turn off, but begins to blink periodically. This can happen due to low voltage in the mains supply, malfunctions in the starting system, or sudden changes. In such cases, the resources required for regulation are reduced stable operation lamps. A decrease in the supply current is allowed within 5%. It is necessary to measure the current strength in the supply network and in case of any deviations, contact the service organization. Such voltage surges have Negative influence not only for the operation of the LED lamp, but also for the entire existing household appliances. The service life of lighting fixtures in this mode can be reduced by more than 20%.
Flickering often occurs due to a malfunction of the trigger system installed in the lamp housing. It is very difficult to replace, and in some cases it is impossible to replace. This condition most often occurs at the end of its service life, which indicates that the lamp is unsuitable for further use. Voltage surges and drops in the network often occur as a result of the use of high-power equipment. Typically this is welders consuming a large number of electricity.
LED lamp blinks when turned off
Quite often there is a phenomenon when the LED lamp continues to blink even when the power is turned off. This usually occurs due to faulty wiring or when using an illuminated switch. Both of these factors lead to the same consequences. As a result of the passage of a small impulse that recharges the starter, flashing occurs LED light bulb. Full startup does not occur due to the small amount of current, so the light turns on for a split second and then goes off.

The simplest solution to the problem is to replace the backlit switch with a regular device. If for some reason this is not possible, it is necessary to install an additional one with a power of 2 W and a resistance of 50 kOhm. Due to it, the necessary resistance will be added, preventing random impulses. The resistor is connected directly near the switch or directly to the lamp. A special heat-shrinkable tube is used to insulate and secure the resistor.

One option would be to replace the single LED bulb located near the voltage entry point with a regular incandescent bulb. It absorbs all impulses and thus prevents blinking. In another case, the backlight is installed independently of the switch, that is, the backlight diode is connected directly to the network. Its glow will be constant, even when the switch is off. The problem may arise due to poor-quality wiring, so it is recommended to check all connections and, if necessary, properly insulate all identified areas.
Fluorescent, users very often encounter an annoying phenomenon - a switched-off lamp flickers in the dark, creating a dim, chaotic flicker.
There is no mysticism in this phenomenon; the reasons why this type of lamp blinks are well known and have a scientific explanation. This article will answer the question of why an energy-saving fluorescent lamp flickers when the switch is off, and will indicate ways to get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon.
Switch backlight
The most common cause of blinking of this type lamps are LED or neon lighting in the switch, which is connected in parallel with the switching contacts, and glows due to the current passing through the load circuit.
To answer why this phenomenon of weak flickering occurs in relation to fluorescent lamps, you need to understand their operating principle. The electronic ballast contains a diode bridge for rectifying the alternating mains voltage and a high-capacity smoothing capacitor.
A small electric current passing through LED backlight, gradually charges the capacitor, raising the voltage level to a value at which the electronic circuit tries to start, while a short-term discharge occurs through the gas filling the bulb of the energy-saving lamp, which causes it to glow briefly and dimly.
Since, due to the switching on of the circuit, the charge on the capacitor quickly runs out, the voltage drops, and the circuit, which did not have time to start normally, stops working again, and the capacitor charging cycle is repeated.
Flickering is not only annoying, but also harms the lamp itself.
It should be noted that such attempts to start electronic ballasts negatively affect the gas condition and reliability electrical diagram in general, which is designed for a certain number of given launches.
Therefore, many manufacturers of energy-saving fluorescent lamps even indicate in the passport of their products a warning about the inadmissibility of using their products in conjunction with a backlit switch.
Naturally, to extend the service life of the electric lighting device, and to remove annoying blinking from your eyes, you need to switch to a regular analogue, or by disassembling the existing one, to disconnect the backlight power circuit. But not in all cases, this replacement or modification may be successful, since the flashing of the lamp can be caused by other reasons, which will be described below.
Much top scores provides bypassing the contacts of an energy-saving lamp socket using a conventional incandescent lamp, in which this microscopic current causes practically no effect - the filament will not heat up even by one degree, not to mention temperatures sufficient for radiation.
But connected in parallel ordinary light bulb, even if low-power spoils overall design and color scheme and violates the very principle of energy saving, and there may simply not be enough space for it if the chandelier is designed to connect one lamp. And in this case there is a way out.

Application of resistor
Removing the phenomenon of a flashing fluorescent lamp occurs due to the fact that electrical resistance, connected in parallel to the incoming terminals of the rectifier bridge, takes all the energy, preventing the smoothing capacitor in the electronic ballast from charging, thereby preventing uncontrolled flashes and blinking.
Therefore, it is not necessary to use an incandescent filament for these purposes - you can use a radio component that has electrical resistance and the necessary parameters for dissipating the heat generation that will occur when the voltage is turned on to operate the lighting. This radio component is called a resistor.
The resistor for bypassing the contacts of the fluorescent lamp socket must have a nominal resistance of 50 kOhm, and a minimum dissipation power of 2 W. As the resistance increases, some of the electricity will charge the electronic ballast capacitor, causing unpleasant lighting effects in the energy-saving lamp, and as the resistance value decreases, the resistor will heat up when the switch is turned on.
For the same reason, you cannot reduce the rated power of the resistor. You can connect the resistor directly to the socket terminals, or to the terminal block connecting the chandelier wires to the wiring coming from the switch. This method, using a resistor will also be effective for other reasons that cause flickering of energy-saving fluorescent lamps.

Wiring like an antenna
The longer the cable from the energy-saving lamp to the switch, the larger area conductor, the potentials that are induced due to the filling of the ether with radio waves of a wide variety of frequencies increase accordingly.
Despite the apparent microscopic nature of these values, it must be remembered that the very first detector radio receivers operated without any power at all, thanks to a large area and extension antenna. Energy accumulated due to the influence of radio waves and electromagnetic induction, was enough to operate a low-power sound source - a telephone earphone.
Electrical vibrations that arose in the antenna and the self-oscillating circuit passed through the detector (diode) and caused vibrations in the earphone membrane. Exactly the same processes, only much more energy-intensive, due to the fact that electrical interference from absolutely all radio frequency spectra participates in the accumulation of charges in the cable, which acts as an antenna (only a radio wave of one frequency worked in the receiver, the rest were suppressed), and the electronic ballast diode bridge performs detector function, also charging the capacitor.
The use of a resistor in this case also helps, but not always - sometimes the radiation can be so strong that the resistor cannot cope with the accumulated potential - this can happen during a thunderstorm, work near an electric welding machine, or even during phone call by mobile phone.
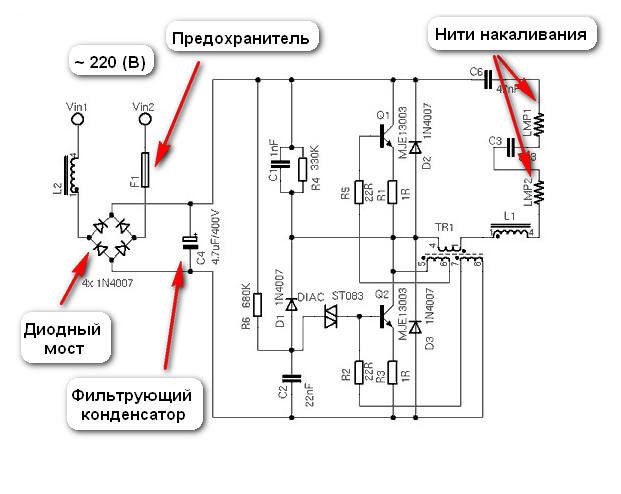
Electrical circuit of an energy-saving lamp
Incorrect phase wire connection
The energy-saving lamp also blinks when the light is off due to incorrect connection of the switch, in which the phase wire goes directly to the lamp, and neutral wire goes into rupture through contacts. In this case, using a shunt resistor will not help.
- Firstly: fluctuations in mains voltage are themselves a source of radio waves;
- secondly: the phase wire can be considered an antenna that extends all the way to the transformer substation;
- thirdly: a small current will flow through the diode bridge circuit, charging the capacitor, due to leaks, calculated in microamperes through the insulation of the wiring going to the switch, and the amount of current flowing through the resistor and the switch backlight (if any, otherwise connect the resistor generally useless) will not be sufficient to neutralize the unpleasant effects of lamp blinking.
In this case the only way get rid of the flickering of a fluorescent lamp - disassemble junction box and do correct connection phase wire to the switch.
In conclusion, it should be added that powerful electromagnetic waves also directly affect the internal elements of energy-saving lamps and cause flickering even in mobile fluorescent lamps that are not connected to the network.
In this case, the manufacturer must schematically level out interference, shield and bypass circuits subject to such influence. Therefore, when choosing a fluorescent lamp from a particular manufacturer, you need to read user forums and ask whether the lamp is blinking due to the influence of radio waves, if other causes of blinking are excluded.
If we compare incandescent lamps and energy-saving lamps, the latter are one step higher. This light source is much better and more progressive. Therefore, incandescent lamps are becoming less and less common, and housekeepers, although several times more expensive, are confidently pushing them out of our homes. Having purchased such a lamp, we have the right to expect impeccable performance from it. This is mostly true, but sometimes energy-saving lamps start to flicker. Why does the energy-saving lamp blink? Our article will answer this question.
The design of an energy-saving lamp includes:
- flask. The form is very different;
- two spirals;
- electronic ballast.
Operation of an energy-saving light bulb
Both fluorescent and energy-saving lamps have the same operating principle:
- A glow discharge occurs between two electrodes placed in a flask into which inert gas and mercury vapor are pumped.
- Invisible ultraviolet radiation mercury atoms, when passing through the walls of the flask, coated on the inside with a phosphor, turn into the light that we see. At the same time, the color of the light is different, it all depends on what composition was used to coat the inside of the lamp.
Interesting: Despite the fact that the voltage in our networks is alternating, the energy-saving lamp operates at constant voltage. The conversion of DC to AC voltage occurs in an electronic ballast using a diode bridge.
Why do energy-saving lamps blink?

Imbued with the idea of saving energy, the man threw out all the familiar old lamps in the house and installed energy-saving ones. And how unpleasant it is when they suddenly start blinking.
Lights flash differently
Energy-saving lamps flash under different circumstances:
- when the switch is on, they blink constantly;
- at the moment of switching on and for some short time after;
- periodically;
- even when the switch is off.
The lamp is off but blinking
Why does the energy-saving lamp blink, because in theory there is no voltage in the network? But it turns out that the problem is not in the lamp, but in the switch with LED or neon backlight. And that's why:
- The power contacts close as soon as we turn off the switch.
- The illuminating lamp begins to burn.
- A very small electric current from the network transits through a lamp, chandelier with energy-saving light bulbs on the ceiling and returns to the network again. In this case, the capacitor in the electronic circuit energy saving light bulbs recharges and the light flashes.
- The capacitor instantly discharges and again everything repeats in a circle. That's the whole secret of the blinking of a switched off energy-saving lamp.
Conclusion: you cannot combine a backlit switch and an energy-saving lamp. Even if flickering doesn't annoy you, think about how much faster your not-so-cheap lamp will wear out. Because of large number launches, it will quickly use up the resource built into it and after a maximum of 2 months it will have to be thrown away.
There may be other reasons, namely:
- errors made during installation of electrical wiring;
- a lamp produced by an unscrupulous manufacturer.
The light flashes when the switch is on
As soon as the light turns on, the light bulb begins to blink. The phenomenon is very unpleasant, but what is its reason:
- The voltage level in the network is so low that the ballast of the energy-saving lamp cannot start it into operation. If so, then take a multimeter, bring it to the outlet and measure the voltage. If there is a deviation from normal (220 V) of 5%, we contact the electricity supply company with a complaint that the quality of the supplied electricity does not meet the established standard. After all, not only light bulbs can fail, but also household appliances.
- The commissioning device for the energy-saving lamp is faulty. There is nothing else left to do but buy a new lamp, because... old renovation is not subject to.
- There are power surges in the network. All claims against the power supply company, unless, of course, you perform welding work by connecting it to the network at home welding inverter. Then that’s the reason, and you can’t do that.
Energy saving lamp flashes after switching on
This phenomenon occurs when you have an energy-saving fluorescent lamp that has electromagnetic system launch. When energy-saving fluorescent lamps malfunction, such as a faulty starter, a slow start occurs. Delay up to 10 sec. still acceptable, but if more, then change the starter.
Eliminating the causes of blinking energy-saving lamps
If, when buying lamps, you put quality at the forefront, and not the most low price, then the issue of malfunction of energy-saving lamps disappears. All that remains is to look for the cause elsewhere and eliminate it:
- The first and easiest way to get rid of the lamp flickering when it is off is to open the backlit switch and open the circuit through which current flows to the lamp. The capacitor will stop being energized and the lamp will stop flashing.
- The second radical method is to change the switch with a light bulb to a regular one.
- The third is a compromise, i.e. and the blinking is eliminated and the backlit switch remains. The small current that recharges the capacitor is neutralized by screwing 1 incandescent light bulb into a chandelier of 2 or several light bulbs. Of course, this will somewhat reduce energy savings, but it will allow the current to be diverted from the capacitor to the filament. There is one more positive point in this method:
- an energy-saving lamp turns on gradually, and an incandescent lamp turns on immediately, which means the chandelier will light up faster;
- The color of the radiation from an energy-saving lamp is not always comfortable, but in combination with the light of a conventional lamp this disadvantage is compensated. By the way, your eyes will be less tired.
4. The fourth method technically duplicates 3, only the addition will not be an incandescent lamp, but a capacitor or a 2 W resistor with a resistance of 50 kOhm as a shunt element. A small current will flow through it, but sufficient for the backlight to work.
High quality energy saving lamps

When buying energy-saving lamps, make it a rule to pay attention to who the manufacturer is. There is no doubt about the quality of the lamps, from such famous manufacturer, like Philips (Philips). These lamps have good characteristics:
- heat generation is insignificant;
- lasts a long time;
- saves energy by 80%;
- turns on without blinking;
- provides luminous flux of 85%.
Another leader in the production of lighting equipment is the German company Osram. This brand is very popular, and lamps from the OSRAM DULUX SUPERSTAR and OSRAM DULUXSTAR series are distinguished by:
- warm, pleasant light, like incandescent light;
- almost instantaneous achievement of the planned luminous flux;
- excellent light output;
- long service life - 15 thousand hours;
- compact attractive design.
Malfunctions of energy-saving lamps
Let's look at what malfunctions of energy-saving lamps happen and how to eliminate them using the example of PHILIPS 6yr 23W ECONOMY.
Disassembling energy-saving lamps
We disassemble the body of the energy-saving lamp in the following sequence:
- take a flat-head screwdriver and, moving carefully around the perimeter, push back the latches;
- disconnect the lamp cylinder by unscrewing the 4 wires with which it is connected to the electronic unit;
- We unsolder the wires connecting the base and the board. The block will remain in your hands. It is now possible to determine the fault.

Common faults:
- If observed on the network increased voltage, then the capacitor will swell and leak, and the lamp will stop lighting. Here it is necessary to replace the CD and test all semiconductors.
- For the same reason, a malfunction such as breakdown of capacitor C5 occurs. The lamp glows only where the filaments are located. We change the capacitor.
- The reason for the lamp not glowing fully can be a fairly long period of operation. In this case, the sealing of the flask is partially broken, and thermionic emission is reduced. We throw away the lamp.
- When one of the filaments burns out, the lamp stops burning. In this case, we check the serviceability of capacitor C5. Where the filament is broken, we unsolder the diode, and in its place we insert a 10 Ohm resistor.
- Another reason for the failure of an energy-saving lamp is a faulty diode thyristor (dinistor). This reason is detected by eliminating the malfunction of semiconductors, capacitors, inductor windings, and filaments. The solution is to replace the faulty element.
- If, by calling resistors and semiconductors, you see that they are out of order, then the parts, of course, must be replaced. But think about whether it’s worth doing this, because such repairs will be expensive. It's easier to buy a new lamp.

Watch how the author of this video eliminates the flickering of an energy-saving lamp:
