Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
1. History of the construction of panel houses
2. Construction of the first large-panel houses in Magnitogorsk
3. Technology of construction of frameless buildings
List of Internet resources
1. HistoryI build panel houses
Since the early 1960s, housing construction in the USSR was based on industrial housing construction - the construction of microdistricts from 5- and 9-story serial panel houses. This reduced the cost of construction and made it possible to increase the supply of housing, and also made it much more comfortable than communal apartments, simply because from now on each apartment was designed based on the occupancy of one family, and not several. Simultaneously with the construction of large-panel houses, mass-produced houses made of “blocks” began to appear - the same panels, but not the entire wall.
“The development of our large-panel construction was preceded by long-term experimental work by Soviet scientists and civil engineers, which began back in 1931-1933.”
These words open the article “On the architecture of large-panel buildings” by K. Zhukov in the magazine Architecture of the USSR No. 9, 1952. In the text, the author notes that in block construction, which preceded panel construction, the USSR was ahead of America. However, back in 1910, in one of the suburbs of New York, the first houses appeared in which large panels made of reinforced concrete were used. In the 20s - 40s of the twentieth century, inexpensive panel houses began to be built in Germany, France and other European countries. In Russia, the mass production of 1-2-story large-panel residential buildings was established during the Great Patriotic War. It was then that the authorities saw large-panel housing construction as a solution to the housing problem.
In 1947, the USSR Academy of Architecture began the development of a fully prefabricated large-panel dwelling. The author of the design of the first apartment buildings of the K-7 project was the Soviet civil engineer Vitaly Lagutenko (by the way, the grandfather of the musician Ilya Lagutenko). At first, the four-story Lagutenkovsky Houses were built with a steel frame, but due to the high consumption of metal, they soon switched to a prefabricated reinforced concrete frame. Since 1950, in addition to frame-panel houses with connected joints, the construction of frameless panel houses began in Moscow, Leningrad, Kyiv, Magnitogorsk and other cities.
The experience was considered successful, and the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 9, 1950 No. 1911 “On reducing construction costs” initiated the design of the first highly mechanized concrete concrete plants.
A large-scale transition to new solutions in the field of construction began with the Resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated August 19, 1954 “On the development of production of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures and parts for construction.” According to this decree, it was necessary to build 402 factories of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures in the Union and organize the production of parts at 200 polygon-type sites.
On July 31, 1957, the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR adopted a resolution “On the development of housing construction in the USSR,” which laid the foundation for new housing construction.
After some time, the fields around the village of Cheryomushki near Moscow became the first practical construction site, where five-story residential buildings were erected in a short time from ready-made house-building structures. According to some information, the first Moscow “Khrushchev” is house number 16 on Grimau Street, built in 1957. The Cheryomushkin construction experience was subsequently extended throughout the country.
According to other sources, at the very beginning of the 1950s, in large industrial centers of the USSR (Moscow, Sverdlovsk, Kuzbass), entire blocks of four-story capital buildings were built, the structures of which were pre-fabricated at the factory.
panel frameless house technology
In 1955, Nikita Khrushchev signed the decree “On the elimination of excesses in design and construction.” The excesses included arches, tower porticos, sculptures and “unacceptably inflated areas of the hallways, corridors and other auxiliary rooms.” Over the next two years, standard designs for prefabricated panel houses were developed.
2. Construction of the first large-panel houses in Magnitogorsk
Construction of the first large-panel house in the USSR began in 1949 in Magnitogorsk according to the designs of the USSR Academy of Architecture and the Magnitostroy trust.
In 1952, a second experimental house was built. Subsequently, the Magnitostroy trust and Gipromez designed and implemented 4-story large-panel houses with transverse load-bearing walls in Magnitogorsk in experimental and mass housing construction.
Projects of large-panel houses of the “Magnitogorsk” type were carried out on the basis of planning solutions for standard brick houses; their buildings have a width of 13.2 meters and dimensions between the transverse load-bearing walls are 3; 3.6 and 4.96 m. All vertical and horizontal loads in the buildings were carried by floors and internal transverse and longitudinal load-bearing walls. External walls were designed as self-supporting structures.
The cutting of the external walls was provided on panels the size of a room. Their outer layer was made of decorative concrete, the inner layer was made of heavy concrete 4 cm thick. The panels were insulated with blocks of non-autoclaved foam concrete with a volumetric weight of 600 kg/m3. The total thickness of the panel is 22 cm. The internal load-bearing panels were made of structural cinder concrete grade 100 with the installation of upper and lower horizontal support strips of heavy concrete.
In the first houses built, the joints of the external panels were covered with wide insulating pilasters; In subsequent construction, the facades of the houses were designed with open seams.
For the floors, panels the size of a room were used, supported on three sides by internal load-bearing walls. They were made in two layers, 12 cm thick, consisting of heavy concrete 3 cm thick, in which the working reinforcement was located, and a layer of slag concrete 9 cm thick.
In 1958, a house-building plant was put into operation in Magnitogorsk, designed to produce sets of products per year for panel houses with a total living area of 30 thousand m2. From this time on, it can be considered that mass construction of frameless large-panel residential buildings with transverse load-bearing walls began in Magnitogorsk.
Experience in the construction of large-panel residential buildings in Magnitogorsk has revealed a significant advantage of frameless structures compared to frame-panel solutions. The use of uniform planar prefabricated products has sharply increased their factory readiness and reduced labor costs for the manufacture and installation of structures. The cost of living space in panel houses turned out to be 10-15% lower than in similar brick houses.
Further in Murmansk Since 1955, the construction of large-panel 4-story residential buildings with transverse load-bearing walls was carried out using design solutions used in Magnitogorsk. The floor panels here were made the size of half a room with open seams on the ceiling.
Also, with minor modifications to the design solutions, residential buildings of the “Magnitogorsk” type were designed and built by Tsentr-Akademstroy in 1957-1959. in New Cheryomushki in Moscow three 5-storey corridor-type large-panel buildings for dormitories.
The experience of building frameless large-panel houses in Magnitogorsk was used in Czechoslovakia, where several dozen large-panel houses with transverse load-bearing walls were built in Gottwald, the suburbs of Prague and Brno.
3. Construction technologyframeless buildings
The external and internal walls of frameless panel buildings are cut into “room-sized” panels. In the standard projects being developed for 4-5-storey residential buildings, the external wall panels have dimensions of length - "per room", height - "per floor" (3.0--3.3 m) and a weight of about 5.0 t. Panels are made with door and window openings. Transverse partitions dividing rooms in frameless houses are usually located opposite the joints of wall panels. There are two design schemes for frameless houses: 1) with load-bearing transverse partitions made of concrete, in this case the floor panels rest on the transverse partitions; 2) with non-load-bearing partitions, which are made from local and low-strength materials (for example, gypsum), and the floor panels rest not on the partitions, but on the longitudinal walls. Due to the large size of the wall panels of frameless houses, they are usually made from lightweight concrete (slag concrete, expanded clay concrete, thermosite concrete) or from cellular materials (foam concrete, aerated concrete, foam silicate). Large wall panels of frameless houses are made with an external textured layer of decorative concrete applied and with an internal surface prepared for painting. At the factory, window and door openings of such panels are filled, window sill boards and drains are installed, and heating devices are installed. Partitions and ceilings in such houses are also made in room size. During manufacturing, wall panels and floor panels of frameless houses are equipped with steel embedded parts, which are welded during installation, which ensures the strength and stability of the building. The installation of panels of frameless houses must be carried out in a certain sequence, ensuring the stability of the structures during installation. The order of installation and fastening of elements is indicated in the installation organization projects.
Panel house components, which are large reinforced concrete slabs that are manufactured in factories. In factory conditions, reinforced concrete products are manufactured according to existing GOST standards, so it is assumed that their quality should differ in a positive direction from products produced directly on the construction site. But in reality, at some factories the proper technology is not followed. The construction of a panel house is reminiscent of assembling a children's construction set. Ready-made parts of the structure are delivered to the construction site, which the builders can only install. As a result, labor productivity in such a building is very high. The construction site area is much smaller than what is needed when building a brick house. Such lengthy and labor-intensive processes as installing reinforcement or concreting, which are typical for monolithic house construction, are completely excluded. This is precisely where experts see the main advantage of panel housing construction over other types of construction. The disadvantages of this type are poor-quality assembly of the structure. The sore spot is the interpanel seams, through which, if done incorrectly, wind and water penetrate. Also, panel houses are characterized by poor sound insulation, in contrast to houses with wooden floors and some types of monolithic houses.
ListInternet resources
1. http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki - typical series of residential buildings
2. http://ria56.ru/posts/kratkaya_istoriya_panelnogo_stroitelstva_v_rossii.htm - Brief history of panel construction in Russia
3. http://bigpicture.ru/?p=470469 - “How the Khrushchev buildings were built”
4. http://inf-remont.ru/design_buildings/dbui5 - Construction of the first large-panel houses in Magnitogorsk
5. http://for-engineer.info/builder/elements/steny-panelnyx-beskarkasnyx-zdanij.html - Engineering reference book
Posted on Allbest.ru
Similar documents
Development of housing construction in the USSR. The history of the emergence of “Khrushchevka” - panel or brick houses that were built in three or five floors, during the reign of Nikita Sergeevich Khrushchev. Renovation and renovation of houses, series of houses and their layouts.
abstract, added 04/29/2015
The concept and types of country houses for temporary residence. Design of country houses and cottages. Regulatory regulation of construction. Foreign experience, Canadian construction technology. Advantages of a frame-panel house. Selection of materials.
course work, added 07/01/2013
Construction technology being developed: clay casting of walls with subsequent modernization of the mortar. Marketing research of Kaliningrad countryside real estate. The advantages of building half-timbered houses, its main stages and cost.
presentation, added 12/14/2010
Construction of apartment buildings in the city of Cherepovets. The relationship between the construction of residential buildings and housing and communal services management companies in the city. Legislative justification for the construction of an apartment building as a construction project. Management of an apartment building.
course work, added 02/14/2010
Characteristics of the area and construction conditions. Space-planning and structural characteristics of residential buildings. Determination of the volume of construction and installation work. Technology for constructing a group of residential buildings. Calculation of resource requirements, master plan.
course work, added 11/14/2017
Design of modern residential or civil facilities. A variety of façade structures of panel buildings and their protection from progressive collapse. Construction of a multi-storey residential building. Development of a series of standard block sections.
test, added 02/02/2016
The main advantages of frame houses made of light thin-walled steel structures. Technology for creating prefabricated buildings. Flow diagram of the production and construction of a building based on LSTK, design solutions and design, assembly and installation.
test, added 03/15/2015
Project for the construction of multi-storey buildings in Samara. Determination of the estimated cost of construction projects. Characteristics of the general contracting construction organization and design of a comprehensive enlarged network schedule for the construction of multi-storey buildings.
practical work, added 04/26/2009
Analysis of modern construction technologies. Features of the Royal Building System method - building structures intended for pouring concrete. The principle of constructing a monolithic building. Frame houses (Canadian technology for constructing wooden houses)
abstract, added 01/14/2010
Technology of construction of wooden houses, features and materials used, requirements for environmental friendliness and strength, quality assessment criteria. The role and features of the bathhouse, stages and principles of its construction. Types of houses, baths, their interior.
Over the past few years, the construction market has been flooded with so-called frame houses, which are erected weekly in huge numbers both by companies and with their own hands. The reason for such love for “frameworks” lies in the ease of construction and the pace of construction. The phased construction of a frame house allows you to assemble a full-fledged residential building in one season, which will look quite presentable, and have an attractive price and cost-effectiveness in maintenance. The technology is easy to understand and implement with your own hands.
What is the essence of construction
As the name implies, the technology consists of forming a kind of frame made of wood (boards or timber) or metal, with gradual, step-by-step covering of it with layers of films, membranes, insulation, etc. This multi-layer wall construction allows one to achieve good thermal characteristics with fairly thin walls.

What materials form the wall?
- mineral wool insulation
- insulation foam sheets
- waterproofing in the form of a film or membrane
- vapor barrier in the form of a diffusion membrane
- OSB sheets
- external and internal finishing

When constructing the building frame, do not forget to make openings for windows. They must be strengthened with crossbars that take the load and distribute it evenly to the foundation. Read more about inserting windows.
After erecting the walls, it is necessary to proceed to the next stage.
Third stage of construction: roofing
Even while designing your house, you should have decided what type of roof will crown your building. Most often, a gable roof is chosen for frame houses, however, single-pitch roofs are also in demand due to the ease of DIY installation, simplicity of design and lower price.

The construction of the roof begins with the rafter system. The rafter system is the main frame of the roof. The rafter system consists of the following elements:
- Mauerlat
- rafter legs
- racks
- runs
- puff
- sill
- struts
- sheathing
When the roof frame is completed, it is necessary to insulate it. The roof filling consists of almost the same layers as the wall. From the outside, we insulate the roof with sheets of foam plastic or mineral wool, lay down waterproofing, which we fix with lathing.

On the inside we put a layer of mineral wool or polystyrene foam if the attic space is not intended to be residential. We fix the vapor barrier layer and cover everything with OSB boards. We cover the roof with roofing materials depending on the slope of the slope and our own preferences. Remember that soft roofing, which has become very popular recently, is laid only on a plane, so the sheathing must be supplemented with OSB boards. In this case, the angle of inclination can be small - from 5 degrees.
Fourth stage of construction: floors
On the ground floor, floors are most often installed on the ground. What does it mean? The technology is as follows. We remove the initially fertile layer of soil and fill it with a layer of gravel. It is necessary for drainage, since moisture will seep inside and have less contact with the cement screed. On the ground we make a layer of sand of 30-50 cm, depending on the height of your foundation. Carry out compaction with your own hands or using equipment. As a result, the sand layer should be located 5 cm below the foundation level to avoid cold bridges and freezing in the corners.

Next, we perform a rough screed using liquid cement. If you take cement that is a little more liquid than for constructing a foundation, you will not have to level it with tools, since under the influence of gravity the cement itself will be evenly distributed over the ground. The most important thing is that the ground is level, otherwise the liquid cement will flow into one place.
When the rough screed is dry, you can continue installing the floor. To do this, we waterproof it with a film, on top of which we lay out the floor insulation. Using a mesh, you can attach underfloor heating pipes (liquid or electric) on top of the insulation. And fill in the finishing screed.
The final part of floor construction is the floor covering. These can be wooden floors, tiles, laminate, etc.
If you do not want to use cement in the construction of the floor (for example, if construction takes place in winter), the technology of constructing wooden frame floors based on logs will help you. How to arrange such a floor, see the diagram:

To set it up you need:
- board 25x100
- timber 200x200
- timber 70x195
- board 50x150
- wind protection
- insulation
- underlay and laminate or tile
You will find more information about flooring in a frame house.
Fifth stage of construction: finishing
At the fifth stage of construction, the external and internal finishing of the house, installation of plumbing, connection of lamps, sockets, heating of the frame house and other work are carried out, which will make a real home for living or recreation from a simple box with walls and a roof.
Since the walls of the frame house are covered with OSB boards, it will not be difficult to carry out external and internal decoration even with your own hands. You can read about how to make external finishing and choose the right materials in our article.

Interior decoration depends primarily on the preferences of the home owners, and can be done using tiles, wallpaper, liquid wallpaper, plaster, in particular decorative. The walls can be painted, covered with clapboard, siding, the ceilings can be whitewashed, or suspended ceiling technology can be used. The floor can be covered with tiles, parquet, laminate. In general, there is room for your imagination to run wild.

By this time, you should already have all the pipes for installing plumbing installed (they are removed during the construction of the floors, during the rough screed), and the electrical wires should be laid out. Construction of a frame house from the first to the fifth stage takes about 3 months.
The supporting frame is the “skeleton” of any house. What it consists of, how it works and what types of load-bearing frames of a private house exist will be discussed in this article.
What is the load-bearing frame of a house?
A load-bearing frame is a set of structural elements (walls, columns, foundations, beams, floors) combined into a single system that provides strength, rigidity and stability of the house. Strength of the supporting frame- this is its ability to resist the influence of loads acting on it (the weight of structures, people, wind, snow, furniture, etc.), without collapsing or receiving critical deflections and deformations. Rigidity of the load-bearing frame- the ability not to change the shape of the frame under the influence of such loads, and sustainability is the resistance to overturning or shearing. The house must be designed in such a way that when exposed to loads, none of these qualities are lost. Note that each structure performs its own separate function (stairs connect floors, walls protect from the street and absorb loads from floors, etc.), sometimes more than one, but as part of the load-bearing frame they are all interconnected and work as a single “skeleton” of the house, that is, the work of structures is considered as a whole.
The need to use a specific type of load-bearing frame of the house is due to:
- Functional factor (depending on the purpose of the premises and the entire house; for example, you want to get a house with an open layout, a lot of undelimited space, for this it is better to use a frame frame, and for a standard cottage with many rooms, a frameless frame with delimitation by walls is suitable);
- Architectural factor (thanks to different types of load-bearing frame, a house can be given architectural expressiveness. For example, a cottage in the “high-tech” style is better and easier to build with a frame load-bearing frame, and a house in the “Russian style” is frameless);
- Technical and economic factor (during design, it is possible to calculate the cost and timing of construction with different types of load-bearing frames, based on the data obtained, make the final decision);
- In addition, the choice depends on what you want the house to be made of (material and wall design). For example, if you decide to build a house with a frameless load-bearing frame, then a foam block wall without additional design solutions (monolithic belts, mesh reinforcement) is impossible.
At the initial stage of designing a cottage, it is very important for the architect and designer to determine what in this case will act as a load-bearing frame, what structures will be its components, how they will be connected, how they will resist loads. Proper combination of all wishes in your home: layout, architectural style, ergonomics of the house, compliance with modern technologies and the requirements of rigidity, strength and stability is the main task for the “architect-constructor” tandem. In this case, the architect will tell and show what your house will be like, and the designer will show with calculations how to implement this idea and which load-bearing frame (there may be several options) is applicable in this case.
Types of supporting frame
At this stage of construction of private houses, there are 3 types of load-bearing frames:
- Frameless (wall) load-bearing frame;
- Frame supporting frame;
- Combined load-bearing frame (incomplete frame).
Descriptions, disadvantages and advantages of each type will be described below.
Frameless (wall) load-bearing frame
This is the most common type in cottage construction. The simplest type of construction of private houses and therefore it is used in the construction of cottages and private houses everywhere. In this case, the load-bearing frame is formed from massive longitudinal and transverse walls connected to the foundation, floors (beams or slabs, more about floors in the article) laid on the walls, stairs (they give rigidity to the frame vertically and horizontally. We can say that the load-bearing frame presented in the form of a rigid and stable box consisting of connected walls and ceilings. The lower part of the walls is usually more massive than the walls of the upper floors, due to the fact that it must support the weight of the overlying ones.
ceilings and walls. For example, the ground floor of a cottage can be made of ceramic bricks 510 mm thick, and the second floor can have thinner walls 380 mm. Thus, the walls should serve as a load-bearing structure and a heat-insulating and enclosing structure.
The walls in this type of frame can be made of brick, reinforced concrete blocks, lightweight concrete blocks, natural stone, wood, etc. The thickness of the load-bearing walls, depending on the material, can be from 250 mm to 700 mm. The thickness of non-load-bearing walls and partitions is from 100mm. Floor slabs are usually prefabricated or monolithic, with a thickness of 150 mm.
The frameless load-bearing frame can be of the following types:
- with longitudinal load-bearing walls
In this case, the basis of the frame is the load-bearing walls, which are located along the long side of a private house, the floors are laid across the house (that is, perpendicular to the walls). The stability and rigidity of such buildings is ensured by flights of stairs, end and transverse walls; the ceilings act as a rigid horizontal diaphragm. The pitch of the longitudinal walls in such houses is usually equal to the length of the floor slab (4.2 m; 5.4 m; 6 m). This type of frame is used in houses with an elongated shape.
- with transverse load-bearing walls
Load-bearing walls are located along the smaller side of the house and the ceilings are laid on them. The walls along the long side of the house can be made non-load-bearing or self-supporting (walls that can withstand the load only from their own weight), but at the same time they must have heat-insulating properties and protect from street temperature. A frame with transverse load-bearing walls has greater transverse rigidity and stability compared to a load-bearing frame with longitudinal load-bearing walls. The disadvantage of this structural system is associated with the inability to vary the width of living quarters, which is once and for all limited by transverse load-bearing walls.
- with longitudinal and transverse load-bearing walls
This scheme is a combination of longitudinal and transverse load-bearing walls; the floors are laid in the longitudinal and transverse directions. Such schemes are applicable for cottages in which the architectural form is difficult to solve using only longitudinal or only transverse load-bearing walls. That is, when the cottage has an unusual shape in plan and it is difficult to solve the space with only longitudinal or only transverse walls.
The rigidity and stability of the load-bearing frame in such houses is ensured by the interconnection of walls and ceilings, flights of stairs (if the flight of stairs is made of monolithic reinforced concrete or metal and is rigidly connected to the load-bearing elements of the frame).
Frame support frame
Until recently, frame buildings were an attribute of industrial construction, but now such load-bearing frames are increasingly being used in private construction.
The frame supporting frame consists of columns, crossbars, ceilings, stairs, and foundations connected into a single system. The columns of the frame are placed both around the perimeter and inside the house; crossbars (beams) are laid on them, which support the floor slabs. Rigidity and stability of such houses are given by rigidity diaphragms (reinforced concrete walls), floors connected to columns, and stairs. They perceive horizontal and vertical loads acting on the house. The walls are self-supporting or suspended (attached to the outer columns of the frame) and perform enclosing and heat-insulating functions. In this way, savings in materials are achieved: load-bearing structures have the thickness required according to structural calculations, and enclosing structures have the thickness calculated according to thermal engineering calculations. The pitch of columns and crossbars in such houses is usually from 3 to 7 m. The thickness of the columns is from 200*200 mm to 500*500 mm, the thickness of the ceiling is from 150 mm.
This type of framework is applicable:
- In houses with an open plan (no partitions at all). Floor layouts may differ, due to the fact that the frame takes on the entire load, and the internal walls serve only to solve the architectural volumes;
- For the construction of houses in seismic areas (Crimea, Carpathians);
- If the architecture of the house specifies a large (5-6 m) distance between the columns or a complex shape of the floor (it is not possible to lay prefabricated floor slabs or it is difficult to carry out masonry).
The frame structure of a private house can be made of concrete structures manufactured at the factory, these are mainly structures for civil engineering, they have certain dimensions, column spacing, section sizes and are difficult to use for private construction. For example, the standard column spacing in civil engineering is 6-9 meters; it is unlikely to be needed in a private house, where the column spacing will not exceed 4-5 meters. Basically, such a frame is made of monolithic reinforced concrete of class B15-B30. The spacing of columns, the height of floors and floors are chosen depending on the architecture of the house and there is no need to “adapt” to standard products. The house in this case consists of a reinforced concrete monolithic frame and self-supporting walls made of lightweight concrete or natural stone (shell rock).


For frame type buildings the following schemes can be used:
- Rigelnaya(the floors rest on crossbars, which are laid on columns. The crossbars are usually 200-400 mm high; due to their height, the useful height of the floor is lost, so this scheme is ineffective in private construction);
- Transomless(usually used in cottages with original layout solutions for plans; in such houses there are no crossbars; the entire load is absorbed by the floors and transferred to the columns. Due to this, the thickness of the floor increases to 200-250 mm).
As the name implies, the frame is a combined model of frame and frameless type. In this case, the load-bearing structures are columns and crossbars (located inside) and massive walls (located around the perimeter). The ceilings rest on the walls at one end and on the crossbars (beams) at the other. Thus, the walls perform a load-bearing and heat-protective function. Columns, in turn, carry only vertical loads. Typically, in private houses with up to three floors, columns are made of ceramic bricks reinforced with reinforcing mesh or reinforced concrete. The stability and rigidity of the house is ensured by shear walls (walls made of reinforced concrete or brick, located along or across the house), stairs (as well as in a frameless frame) and floors connected to walls and columns.
This type of framework is applicable:
- If you want to rationally use the space, but at the same time there is a need for massive walls around the perimeter of the house to ensure thermal insulation;
- In houses using “permanent foam formwork” technology.
The combined load-bearing frame allows you to effectively use the area of the cottage and divide the living space as you wish. For example, on the first floor of the house you decided to make a spacious hall and a large living room, and on the second floor there are bedrooms and a study with the help of a combined load-bearing frame you can easily solve this layout. Floor slabs can be prefabricated reinforced concrete or monolithic. The material for these types of buildings can be reinforced concrete, brick, ceramic blocks, wood, etc. Column sizes from 200*200 mm to 500*500 mm, load-bearing wall thickness from 380 mm, floor thickness from 150 mm (monolithic floor) or 220 mm (prefabricated slab).
Examples of designing a load-bearing frame
Now, using several examples, I will show you how you can make a choice for your future home. I will set a condition in the form of several phrases describing the house and immediately give a diagram of the supporting frame to bring such a scheme to life.
Condition No. 1. The future house should have massive walls made of clay bricks, which will protect it from temperature influences and give the appearance of an “English house”. The foundations should be monolithic, since I know the technology of their construction and it will be easy for me to calculate the costs.
Support frame options
The simplest and most reliable supporting frame for such a house would be frameless load-bearing frame with load-bearing transverse and longitudinal walls. The walls will serve structurally (bear the load) and decoratively (give the desired style. Under such walls it is simple and economical to install a strip foundation, which meets the 2nd requirement.
The supporting frame naturally suggests itself in the form monolithic frame frame, with the help of such a design scheme it is easy to create a flat roof and allow the owner of the house to use it. A clear (rectangular or square) grid of columns and crossbars will enable the owner to complete it in a given style.
- Condition No. 3. It is necessary to create a project for a house for 2 families. The house will be located along the street and have 2 separate entrances. Wall material - brick or foam concrete.
Well suited for this type of home frameless load-bearing frame with longitudinal load-bearing brick walls. Floor slabs will be laid on load-bearing walls. A flight of stairs will add rigidity to the house.
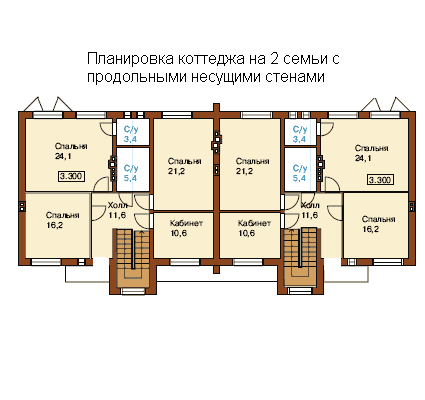
- Condition No. 4. On the ground floor it is necessary to create a lot of free space, without walls or partitions. The floors should be monolithic due to the impossibility of using prefabricated floor slabs.
As stated above, you can apply here combined load-bearing frame. The role of load-bearing structures will be performed by monolithic reinforced concrete columns (in the middle of the house) and main walls (along its perimeter). Columns can be easily connected to monolithic floors and walls, thus ensuring the rigidity and stability of the building.
Thus, each type of load-bearing frame provides its own positive and negative features. When choosing it, at the very beginning of design, it is necessary to clearly understand what type of house and what parameters you want to get in the end.
Nowadays, the full-fledged arched structure of a residential building is increasingly becoming of interest to architects and designers.
Nowadays, the industry is building a lot of prefabricated frameless arched hangars and warehouses made of steel on lightweight types of foundations. However, a frameless arched house made of steel requires high costs for insulation.
Arched house - design features and advantages
Nowadays, arched small houses of a country or garden type are gaining popularity (for example, like), which, if very desired, can even be transported from place to place photo 1. These houses have the shape of a pointed arch in the Gothic style.
Photo 1. Small arched houses
Let's take a quick look at these arched houses. In arched houses, the load-bearing elements of the frame are curved trusses and arches, photo 2, which can be made from:
- become;
- reinforced concrete (extremely rare);
- wood

Photo 2. Structures of an arched house
Features of arched houses
1 .Enclosing structure the house has good thermal performance due to the use of insulation with a thickness of at least 100 mm. The following is used as insulation:
- polyurethane foam (PPU) - recommended thickness of at least 80 mm;
- mineral wool;
- glass wool;
- Interior decoration of the house, photo 3.
Typically, the interior decoration of a house is made from the following materials:
- wooden lining;
- laminated fiberboard;
- plywood;
- OSB boards.
- Exterior decoration of the house.
Typically, the exterior decoration of a house is made from the following materials:
- metal profile;
- soft bitumen shingles;
- wooden shingles;
- roofing made of galvanized steel sheets;
The roof covering in the form of galvanized steel increases the strength and rigidity of the entire roof structure.

Photo 3. Interior decoration of arched houses
- Type of flooring. Usually in such houses they try to arrange the floor from wooden boards, but other types of flooring can be used without problems ( | | ).
- Windows and doors made from:
- wood;
- metal-plastic.
- Foundation the following is used for arched light houses, photo 4:
- columnar (including TISE foundation);
- monolithic slab.

Photo 4. Types of foundations: a) pile-screw; b) tape; c) monolithic slab
Advantages of small arched houses
- Sufficiently high strength of the house and resistance to weather influences, for example, strong wind, hail, snow load, etc.
- Low fuel consumption, warms up quickly and retains heat (low heat loss).
- Savings on cooling the air in the house in the summer, since the house practically does not heat up from the sun.
- Beautiful and original shape of the house.
- Lightweight design.
The dimensions of an arched house vary, the most common are:
- width – 2.4…4.5;
- length – 3.6….6 m (not limited);
- height – 2.4…5 m.
Arched houses of this type can be built either on one level with relatively high ceilings, or on two levels. On photo 5 The layout options for such arched houses are given.

Photo 5. Layout of an arched house
Arched houses can be not only small, light and temporary, but also large, expensive and massive, photo 6.
For example, in the suburbs of New York, a huge arched house with an area of 890 m2 was built worth $3,500,000, photo 7. A house made of concrete, glass and steel.

When constructing hangar premises, high speed of construction and ease of use of the premises play an important role. That is why frameless hangars can satisfy any owner. The technology for constructing this structure is quite simple, as is the method for dismantling and moving the hangar to another location. Despite the fact that the cost of producing frameless hangars is much cheaper than frame construction, these buildings are characterized by high levels of strength, reliability and durability. That is why many of our compatriots are interested in how to build a frameless hangar with their own hands.
Purpose of a frameless hangar
Previously, hangars were used only as parking for aircraft. But today the range of their purposes has expanded greatly. Today, the hangar is not just for airplanes. Frameless hangars are in great demand, especially in recent years, as they solve the problems of locating small and medium-sized enterprises that produce and store raw materials or products.
The main qualities of this structure are a covered metal structure with a large area. Most people use hangars for sports complexes and facilities, shopping centers, roofs, unique projects of private houses, attics and garages. A frameless hangar can also be useful for commercial purposes, for example, for exhibition halls, repair stations and workshops.

In the industrial sphere, frameless hangars are also used quite often - as industrial warehouses, agricultural machinery stations, production facilities, and storage of agricultural products. Aircraft hangars, food warehouses and barracks are very popular in the military industry. Quite often, a hangar is used to store grain or other products.
The construction of warehouse structures must comply with established requirements that take into account the safety of various products. Depending on building regulations, the hangar may have different configurations. Some options must have windows, doors, gates, a mechanized system, etc. Structures can move and move apart. Warehouses must provide adequate ventilation and air conditioning.
Types of frameless hangars
Nowadays, frameless hangars are made of metal structures that are covered with an awning or sheathed with a special coating. Therefore, frameless hangars can have many configuration options.
The cold hangar is performed in the usual way. It is made from a metal profile or covered with a special tarpaulin fabric. As a rule, such a hangar is intended for storing equipment or machinery, as well as for short-term storage of goods.

An insulated hangar is built a little differently. Mineral wool is placed between the double arch for insulation. Then everything is filled with special foam. Typically, frameless arched hangars are built in areas with difficult climatic conditions. It is also better to use the insulated option for storing products that require it.
The equipment of the room largely depends on its intended purpose: gates, awnings, crane, beams, stained glass windows, gates, partitions, glazing. Construction kits can be expanded according to the owners' requirements. Remember that the hangar must meet not only the established rules and regulations, but also the comfort and technical equipment of the staff. A high-quality hangar must certainly have modern security systems.
Advantages of frameless hangars
When erecting a frame building, it is necessary to construct complex load-bearing elements, additional supports and beam structures. But in the construction of frameless hangars, self-supporting structures are used, which are more profitable and practical in terms of economic indicators and functional parameters. Let's take a closer look at the advantages of frameless hangars:
- Easy to install and disassemble. To build a frameless room, you do not need to have qualified knowledge. In addition, you will spend much less time building a hangar than building a building made of brick or reinforced concrete. Due to the lightness of the metal structure, you can not lay a powerful foundation, but use screw piles for it. The advantage of quickly dismantling the hangar is that you can move it to a more convenient location. This feature makes the frameless hangar mobile.
- Structural strength. Despite the apparent lightness, tests have confirmed the good strength of frameless structures. The absence of nuts, bolts and sealing materials allows the structure to be used without repairs for more than thirty years. Such a structure can withstand a volume of snow cover of up to 480 kilograms per square meter and high wind speeds, up to approximately 200 kilometers per hour, at temperatures from minus 50 to plus 50 degrees Celsius. Therefore, such structures are very stable. They are also waterproof and fireproof.
- High speed of construction. Often, parts for a frameless hangar are delivered already assembled, so a modern model can be built in the shortest possible time. Arched profiles are made immediately on the construction site using a sheet bending machine. Transportation of equipment is very simple, which makes it possible to work even in hard-to-reach areas.
- Economical. Hangars are erected quite quickly; they do not require additional fastening materials, waterproofing, etc. The price of frameless arched hangars is 2 times lower than the cost of frame structures. By choosing a frameless hangar, you save your time and money. The latest construction technologies without frames make it easy to complete this structure yourself.

Myths about frameless hangar
When choosing a hangar structure, people are often afraid of frameless structures because they consider them to be of lower quality. We tried to dispel all the myths regarding frameless structures so that you can make the most convenient decision for yourself.
Myth No. 1. You can make a frame hangar, which will cost less than a frameless one. Companies that offer the construction of hangars with a frame often cheat and name the cost of the frame itself. But to this price should be added the foundation, construction and installation work, costs for corrugated sheets, and logistics. In addition, the frame structure must be additionally insulated from sounds and water. In frameless hangars, all structural elements are simply connected to each other and rolled, so the cost of a frameless hangar is quite affordable. This approach ensures 100% tightness without extra costs.
Myth No. 2. To organize a warehouse, it is much more profitable to use frame-type hangars. When arranging a warehouse, the use of hangars with straight walls is more convenient because it allows you to use the entire internal space. For this reason, the difference in cost was calculated. It was found that it is more economically profitable to build structures without a frame. Frameless construction requires additional space, but is still half the price. Hangars built without a frame quickly pay for themselves, so they are a more profitable option.
Myth No. 3. Frame-type hangars are much stronger and more durable. A massive metal frame undoubtedly increases the strength of the structure, but entails additional costs. It is known that the price of frameless hangars is two times lower than that of frame ones. In addition, if you make a frameless hangar according to all state standards, the resulting parameters will withstand all the loads of wind and snow. Frameless structures do not have to be repaired and maintained frequently. Thanks to the galvanized steel used, you can further save on corrosion treatment.
Myth No. 4. Frame-type hangars are built faster. For frame structures it is necessary to build a deep foundation. Next you need to install the frame, walls and roof. For frameless hangars, the foundation need not be laid. It mainly serves for the aesthetics of the room. You just need to mount an arched structure, each element of which is load-bearing and enclosing, and then install it.
Frameless hangar construction technology
The finished hangar is a structure made of a special metal profile. Frameless hangars are distinguished by the fact that they do not have a supporting frame. Instead, prefabricated hangars use a metal arch. This is what is used as the basis. The owner himself determines the radius and quantity, and the height and length are calculated according to the selected parameters.
The spans of a standard hangar can range from 8 to 24 meters, and the height will depend on the width of the arch and range from 4 to 12 meters, respectively. The installation of a hangar begins with the installation of the foundation, and the next work consists of installing building profiles on the base. Thanks to the simple assembly technology, the hangar without a frame is very light, so the structure does not require a heavy foundation.

When rolling arched profiles from galvanized steel sheet, a special technology is used that prevents corrosion and increases the service life of the room. The machine mechanism that shapes the profile first creates a straight profile. Subsequent actions form the required bend. Next comes the assembly of the structure on site. This is very convenient, but you must understand that it is very important to comply with increased reliability indicators.
After all, the structure is relatively light, but at the same time it must withstand increased loads of wind, snow, etc. When building a frameless arched hangar, special attention should be paid to the floor, which must be very durable. If you plan to work in an indoor production area, the level of sound insulation should be as high as possible.
Frameless hangar project
The first step is to prepare a project for the future hangar. You must think things through carefully. There should be no hills, ravines or sources of water in the area where the structure is located. Decide in advance on the size, number of floors, etc. The design may include windows and ventilation outlets. Often the hangar dome is made transparent using organic glass, special panels or cellular polycarbonate. This approach will allow you to save on room lighting.
During design, do not forget to take into account the requirements that apply to certain types of products. In some cases, hangars can be equipped with additional premises, for example, offices, locker rooms, showers, canteens and staff rest rooms.
Laying the foundation for the hangar
Almost all types of foundations can be laid under frameless hangars, as in the photo of frameless hangars. The type of foundation should be determined by the size of the weights, the quality of the soil at the base of the foundation, as well as the type and weight of the structures that are used in building materials, the risk of frost heaving, etc. For frameless hangars, you should not install a deep foundation.
As a rule, a shallow slab or strip type base is used. To do this you need to dig a trench. For the cushion, you can use medium or coarse gravel, slag or crushed stone, as well as other similar materials. After laying the pillow, you can begin pouring the foundation. If you plan to make a reinforced concrete foundation, you should install a reinforcement cage before pouring.

Please note that the reinforcement should not touch the formwork walls. Prepare the solution and begin to gradually fill the base. It is very important to compact it after pouring so that there are no air bubbles left there, which could lead to destruction in the future. If it is very hot outside, the surface should be wetted regularly. But if it rains, you should immediately cover the surface.
Construction of a frameless hangar
For the next step you will need rolled galvanized steel in the required quantity. You can order this material from professional builders. They will bring it to the site, after which all you have to do is assemble the structure. The arches must be connected to each other and installed on a supporting metal frame. They are stitched using a beading machine. This method will make the future room waterproof.

If you make a welded connection, it will be almost impossible to move the hangar. After this, it is necessary to install doors and windows, utilities, etc. Subsequently, you can install heating and electricity in the hangar. Engineering communications are carried out depending on the intended purpose of the hangar. It may be necessary to install sewerage, ventilation, security system, water and electricity supply, heating, communications, control and accounting systems. You can use profile flooring as a covering.
Insulation of a frameless hangar
Condensation can accumulate inside a frameless hangar and flow down the walls onto the floor or drip from the ceiling. This phenomenon often occurs in winter, when there is a significant difference in temperature between outside and inside. To avoid this, you should insulate the frameless hangar yourself, which can be done in several ways.
You can insulate using overlays, for example, fastening on hangers or hooks. Polyurethane foam can be sprayed between the inner and outer shells of buildings. You can also lay insulation between the inner and outer shells of buildings, or install a sandwich panel with various fillers.
For insulation, you can use almost all types of thermal insulation materials. The thermal characteristics of the building will depend on the type and thickness of the insulation. To prevent water vapor from penetrating into the insulation, it is recommended to lay the vapor barrier film in one layer. At the final stage, you need to find tarpaulin fabric. You can use old leftovers or material that has already been in use.

These flaps must be sewn together to form a dome. After this, the fabric should be treated with a special solution to make it waterproof. The sewn dome should be placed in a 40% solution with laundry soap and left there for a while. When the fabric is completely saturated, it should be transferred to a 20% solution of copper sulfate. Let the fabric soak well and then dry. After this, you should place a tarpaulin cloth soaked in a special solution on the insulation.
Currently, frameless hangars are considered the most cost-effective and popular type of buildings that can be used for various purposes. Without additional knowledge and skills, you can easily assemble the structure yourself. A frameless hangar will cost you 2 times less than the construction of a frame structure, but at the same time it will not be inferior to the latter in terms of strength, reliability, tightness and durability. We hope that the information provided will help you understand construction technology and make a high-quality structure!
If you decide to entrust the construction of a hangar to professionals, contact TSK "Contractor", their website is tsk38.ru
Here is a video of the process of creating a hangar from TSK "Contractor":
